Differential Inflammatory Responses in Adult and Pediatric COVID-19 Patients: Implications for Long-Term Consequences and Anti-Inflammatory Treatment
- PMID: 38816982
- PMCID: PMC11149468
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.944052
Differential Inflammatory Responses in Adult and Pediatric COVID-19 Patients: Implications for Long-Term Consequences and Anti-Inflammatory Treatment
Abstract
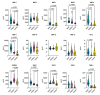
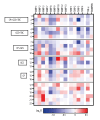
BACKGROUND COVID-19 manifests with varying degrees of severity across different age groups; adults typically experience more severe symptoms than children. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), known for their role in tissue remodeling and immune responses, may contribute to the pathophysiological disparities observed between these groups. We sought to delineate differences in serum MMP profiles between adult and pediatric COVID-19 patients, assess the influence of anti-inflammatory treatment on MMP levels, and examine potential implications for long-term consequences. MATERIAL AND METHODS Serum samples from adult and pediatric COVID-19 patients, alongside controls, were analyzed for MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-7, MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-10, MMP-12, MMP-13, EMMPRIN, TNF-alpha, TIMP-1, TIMP-2, TIMP-3, and TIMP-4. A subset of adult patients received treatment with glucocorticoids, tocilizumab, and convalescent plasma, and MMP levels were compared with those of untreated patients. RESULTS Elevated levels of MMP-1, MMP-7, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 were observed in adult and pediatric patients. Adult patients displayed higher concentrations of MMP-3, MMP-8, MMP-9, TNF-alpha, and TIMP-4 than children. Post-treatment reduction in MMP-1, MMP-8, MMP-9 levels was observed, with median decreases from 21% to 70%. MMP-3 and MMP-7 remained largely unchanged, and MMP-2 concentrations increased after treatment. Notably, anti-inflammatory treatment correlated with reduced post-treatment MMP levels, suggesting potential therapeutic benefit. CONCLUSIONS Distinctive inflammatory responses in COVID-19 were evident between adults and children. While certain MMPs exhibited post-treatment reduction, the persistence of elevated levels raises concerns about potential long-term consequences, including lung fibrosis. Our findings emphasize the need for personalized treatment strategies and further investigation into the dynamics of MMP regulation in COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Serum MMPs 7-9 and their inhibitors during glucocorticoid and anti-TNF-α therapy in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2012 Jul;47(7):785-94. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2012.677954. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22519363
-
Liver and serum expression of matrix metalloproteinases in asymptomatic pediatric liver transplant recipients.Transpl Int. 2017 Feb;30(2):124-133. doi: 10.1111/tri.12879. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Transpl Int. 2017. PMID: 27774663
-
Liver Fibrosis in HCV Monoinfected and HIV/HCV Coinfected Patients: Dysregulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) and Their Tissue Inhibitors TIMPs and Effect of HCV Protease Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Mar 26;17(4):455. doi: 10.3390/ijms17040455. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27023536 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases in the restorative proctocolectomy pouch of pediatric ulcerative colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug 14;18(30):4028-36. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.4028. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22912554 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence review for baricitinib: NICE COVID-19 rapid guideline: managing COVID-19: Evidence review L.London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); 2022 May. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); 2022 May. PMID: 39401305 Free Books & Documents. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 in Children and Vitamin D.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 14;25(22):12205. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212205. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burrage PS, Mix KS, Brinckerhoff CE. Matrix metalloproteinases: Role in arthritis. Front Biosci J Virtual Libr. 2006;11:529–43. - PubMed
-
- Khalid U, Dimov D, Vlaykova T. Matrix metalloproteinases in COVID-19: Underlying significance. Biotechnol Equip. 2023;37(1):295–301.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

