A bibliometric analysis of the 100 most-influential papers in the field of anti-diabetic drugs
- PMID: 38817363
- PMCID: PMC11137835
- DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2023-0230
A bibliometric analysis of the 100 most-influential papers in the field of anti-diabetic drugs
Abstract
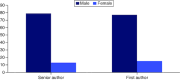
Aim: We analyzed the 100 most-cited articles on all anti-diabetic drugs. A comprehensive literature review found no bibliometrics on this. Methods: Two researchers independently extracted articles from Scopus and ranked them by citation count as the 'top 100 most-cited'. Results: The median number of citations is 1385.5. Most articles are from the USA (n = 59). Insulin has the most papers (n = 24). Majority (n = 76) were privately funded and contained at least one conflict of interest (n = 66). The New England Journal of Medicine has the most publications (n = 44). Male authors made majority of both first and last authorship positions. Conclusion: This study aims to aid in directing future research and in reducing biases.
Keywords: antidiabetic drugs; bibliometric analysis; biomedical trends; diabetes; gender bias.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests or relevant affiliations with any organization or entity with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures
References
-
- Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of Type II diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 14(2), 88–98 (2018). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources