Traditional Chinese herbal formulas modulate gut microbiome and improve insomnia in patients with distinct syndrome types: insights from an interventional clinical study
- PMID: 38817449
- PMCID: PMC11137223
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1395267
Traditional Chinese herbal formulas modulate gut microbiome and improve insomnia in patients with distinct syndrome types: insights from an interventional clinical study
Abstract
Background: Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) comprising herbal formulas has been used for millennia to treat various diseases, such as insomnia, based on distinct syndrome types. Although TCM has been proposed to be effective in insomnia through gut microbiota modulation in animal models, human studies remain limited. Therefore, this study employs machine learning and integrative network techniques to elucidate the role of the gut microbiome in the efficacies of two TCM formulas - center-supplementing and qi-boosting decoction (CSQBD) and spleen-tonifying and yin heat-clearing decoction (STYHCD) - in treating insomnia patients diagnosed with spleen qi deficiency and spleen qi deficiency with stomach heat.
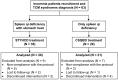
Methods: Sixty-three insomnia patients with these two specific TCM syndromes were enrolled and treated with CSQBD or STYHCD for 4 weeks. Sleep quality was assessed using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) and Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) every 2 weeks. In addition, variations in gut microbiota were evaluated through 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Stress and inflammatory markers were measured pre- and post-treatment.
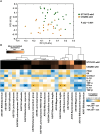
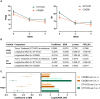
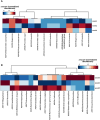
Results: At baseline, patients exhibiting only spleen qi deficiency showed slightly lesser severe insomnia, lower IFN-α levels, and higher cortisol levels than those with spleen qi deficiency with stomach heat. Both TCM syndromes displayed distinct gut microbiome profiles despite baseline adjustment of PSQI, ISI, and IFN-α scores. The nested stratified 10-fold cross-validated random forest classifier showed that patients with spleen qi deficiency had a higher abundance of Bifidobacterium longum than those with spleen qi deficiency with stomach heat, negatively associated with plasma IFN-α concentration. Both CSQBD and STYHCD treatments significantly improved sleep quality within 2 weeks, which lasted throughout the study. Moreover, the gut microbiome and inflammatory markers were significantly altered post-treatment. The longitudinal integrative network analysis revealed interconnections between sleep quality, gut microbes, such as Phascolarctobacterium and Ruminococcaceae, and inflammatory markers.
Conclusion: This study reveals distinct microbiome profiles associated with different TCM syndrome types and underscores the link between the gut microbiome and efficacies of Chinese herbal formulas in improving insomnia. These findings deepen our understanding of the gut-brain axis in relation to insomnia and pave the way for precision treatment approaches leveraging TCM herbal remedies.
Keywords: gut microbiome; gut-brain axis; herbal formula; insomnia; longitudinal integrative network; traditional Chinese medicine syndrome.
Copyright © 2024 Zeng, Xu, Zheng, Zhan, Fang, Li, Zhao, Xiao, Zheng, Li and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and mechanism of Tiaoshu Anshen Decoction in treating insomnia with spleen and stomach Qi dysfunction: A retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 1;103(44):e40160. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040160. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39495997 Free PMC article.
-
FMT and TCM to treat diarrhoeal irritable bowel syndrome with induced spleen deficiency syndrome- microbiomic and metabolomic insights.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Oct 26;24(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03592-y. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39455910 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Zhenjingdingzhi decoction in treating insomnia with Qi-deficiency of heart and gallbladder: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial.J Tradit Chin Med. 2015 Aug;35(4):381-8. doi: 10.1016/s0254-6272(15)30113-8. J Tradit Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 26427106 Clinical Trial.
-
Gut microbiota: A new target of traditional Chinese medicine for insomnia.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Apr;160:114344. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114344. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36738504 Review.
-
[Heart failure: innovative understanding from traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and treatment with classic TCM formulas].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Dec;49(23):6521-6532. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240814.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39805798 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Characteristics and influencing factors of gut microbiota in population with sleep disorders.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 10;16:1586864. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1586864. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40708920 Free PMC article.
-
The integration of machine learning into traditional Chinese medicine.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Aug;15(8):101157. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101157. Epub 2024 Dec 4. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40823261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges in integrating traditional Chinese medicine and gut microbiota research for insomnia treatment.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Oct 16;12(29):6271-6274. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i29.6271. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39417049 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota: a new target for the prevention and treatment of insomnia using Chinese herbal medicines and their active components.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 6;16:1572007. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1572007. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40395724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qu-zhuo-tong-bi decoction exerts gouty arthritis therapy by skewing macrophage polarization through butanoate metabolism.Chin Med. 2025 Jul 22;20(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01162-6. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40696369 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

