Acupuncture combined with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for the treatment of post-stroke depression: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis based on a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 38817548
- PMCID: PMC11137222
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1360437
Acupuncture combined with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for the treatment of post-stroke depression: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis based on a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to systematically assess the efficacy of combining acupuncture with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in treating post-stroke depression (PSD).
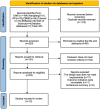
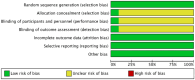
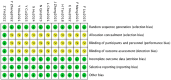
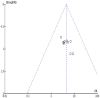
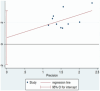
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of eight major domestic and international databases, including the China Knowledge Network, from inception until December 2023. Included were randomized controlled trials that investigated acupuncture combined with rTMS for PSD. The screening process adhered to predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria, and study quality was assessed using Cochrane Handbook 5.1 guidelines. Meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan 5.4 software.
Results: Twelve studies involving 800 patients were included in the analysis. The meta-analysis showed that acupuncture combined with rTMS significantly improved the clinical effectiveness rate (RR = 1.19, 95% CI: 1.12 to 1.27, p < 0.00001) and reduced scores on several scales: Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD) (MD = -3.35, 95% CI: -3.79 to -2.90, p < 0.00001), Self-Depression Scale (SDS) (MD = -9.57, 95% CI: -12.26 to -6.89, p < 0.00001), Chinese Medicine Symptom Score (MD = -3.34, 95% CI: -3.76 to -2.91, p < 0.00001), Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Scale (MD = -3.91, 95% CI: -4.58 to -3.25, p < 0.00001), and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) (MD = -2.77, 95% CI: -3.21 to -2.32, p < 0.00001). Furthermore, acupuncture combined with rTMS treatment improved cognitive functioning (MMSE, MoCA scores) (p < 0.00001) and ability to perform activities of daily living scores (MD = 10.40, 95% CI: 9.53 to 11.28, p < 0.00001). Additionally, it was found to reduce interleukin 6, tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1β, and increase 5-hydroxytryptamine and brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Acupuncture combined with rTMS therapy is recommended for treating PSD, as it effectively improves clinical outcomes, alleviates depressive symptoms, enhances cognitive function, and daily living capabilities, and modulates inflammatory responses and neurotransmitter levels. However, it is important to note that the limitations of the sample size and quality of the included studies warrant the need for more high-quality research to validate these conclusions.
Systematic review registration: INPLASY, Identifier INPLASY202430085.
Keywords: acupuncture; meta-analysis; post-stroke depression; repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; systematic review.
Copyright © 2024 Xiao, Li, Hu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


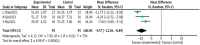
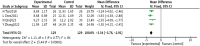





Similar articles
-
[Acupuncture combined with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for post-stroke depression: a randomized controlled trial].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022 Nov 12;42(11):1216-20. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20211221-0002. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022. PMID: 36397217 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Efficacy of non-invasive brain stimulation for post-stroke sleep disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 30;15:1420363. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1420363. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39539650 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of low-frequency rTMS combined with antidepressants on depression in patients with post-stroke depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2023 May 19;14:1168333. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1168333. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37273720 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness Evaluation of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Therapy Combined with Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction for People with Post-Stroke Depression: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 4;20(2):930. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20020930. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36673684 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of combination scalp acupuncture for post-stroke cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurosci. 2024 Nov 29;18:1468331. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1468331. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39678533 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The efficacy and neuroplasticity of Tuina combined with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke depression: study protocol for a single-center, randomized, controlled trial.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1576620. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1576620. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40777856 Free PMC article.
-
Post-stroke depression: exploring gut microbiota-mediated barrier dysfunction through immune regulation.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 3;16:1547365. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1547365. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40098959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term electroacupuncture and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation differentially slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease in AppNL-G-F mice.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Jun 23;17(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01781-z. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40551158 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Efficacy of Acupuncture Combined with Escitalopram Oxalate in the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate Post-Stroke Depression.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2025 Apr 17;21:917-925. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S507265. eCollection 2025. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2025. PMID: 40260315 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

