Evaluating the predictive value of angiogenesis-related genes for prognosis and immunotherapy response in prostate adenocarcinoma using machine learning and experimental approaches
- PMID: 38817605
- PMCID: PMC11137278
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1416914
Evaluating the predictive value of angiogenesis-related genes for prognosis and immunotherapy response in prostate adenocarcinoma using machine learning and experimental approaches
Abstract
Background: Angiogenesis, the process of forming new blood vessels from pre-existing ones, plays a crucial role in the development and advancement of cancer. Although blocking angiogenesis has shown success in treating different types of solid tumors, its relevance in prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) has not been thoroughly investigated.
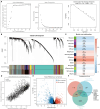
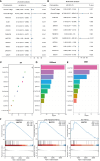
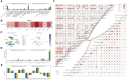
Method: This study utilized the WGCNA method to identify angiogenesis-related genes and assessed their diagnostic and prognostic value in patients with PRAD through cluster analysis. A diagnostic model was constructed using multiple machine learning techniques, while a prognostic model was developed employing the LASSO algorithm, underscoring the relevance of angiogenesis-related genes in PRAD. Further analysis identified MAP7D3 as the most significant prognostic gene among angiogenesis-related genes using multivariate Cox regression analysis and various machine learning algorithms. The study also investigated the correlation between MAP7D3 and immune infiltration as well as drug sensitivity in PRAD. Molecular docking analysis was conducted to assess the binding affinity of MAP7D3 to angiogenic drugs. Immunohistochemistry analysis of 60 PRAD tissue samples confirmed the expression and prognostic value of MAP7D3.
Result: Overall, the study identified 10 key angiogenesis-related genes through WGCNA and demonstrated their potential prognostic and immune-related implications in PRAD patients. MAP7D3 is found to be closely associated with the prognosis of PRAD and its response to immunotherapy. Through molecular docking studies, it was revealed that MAP7D3 exhibits a high binding affinity to angiogenic drugs. Furthermore, experimental data confirmed the upregulation of MAP7D3 in PRAD, correlating with a poorer prognosis.
Conclusion: Our study confirmed the important role of angiogenesis-related genes in PRAD and identified a new angiogenesis-related target MAP7D3.
Keywords: PRAD; angiogenesis; biomarker; machine learning; prognosis.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, He, Zhao, Bo, Zhou, Sun, Ding and Ren.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Multi-omics analysis and experimental validation of the value of monocyte-associated features in prostate cancer prognosis and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 14;15:1426474. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1426474. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38947325 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cancer stem cell-related genes through single cells and machine learning for predicting prostate cancer prognosis and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1464698. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1464698. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39267762 Free PMC article.
-
The role of endothelial cell-related gene COL1A1 in prostate cancer diagnosis and immunotherapy: insights from machine learning and single-cell analysis.Biol Direct. 2025 Jan 8;20(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00591-x. Biol Direct. 2025. PMID: 39780278 Free PMC article.
-
Immune infiltration phenotypes of prostate adenocarcinoma and their clinical implications.Cancer Med. 2021 Aug;10(15):5358-5374. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4063. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34128342 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the gene signatures related to NK/T cell communication to evaluate the tumor microenvironment and prognostic outcomes of patients with prostate adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1564784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1564784. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40308606 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Circulating cell-free DNA methylation analysis of pancreatic cancer patients for early noninvasive diagnosis.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 10;15:1552426. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1552426. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40129923 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating single cell analysis and machine learning methods reveals stem cell-related gene S100A10 as an important target for prediction of liver cancer diagnosis and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1534723. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1534723. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39840058 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in targeted and immunotherapy strategies for glioma: toward precision treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 14;15:1537013. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1537013. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39877359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The gut microbiome, immune modulation, and cognitive decline: insights on the gut-brain axis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 22;16:1529958. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1529958. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39911400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 26;16:1556209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1556209. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40079009 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun L, Tuo Z, Chen X, Wang H, Lyu Z, Li G. Identification of cell differentiation trajectory-related gene signature to reveal the prognostic significance and immune landscape in prostate cancer based on multiomics analysis. Heliyon. (2024):e27628. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27628 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ma B, Qin L, Sun Z, Wang J, Tran LJ, Zhang J, et al. . The single-cell evolution trajectory presented different hypoxia heterogeneity to reveal the carcinogenesis of genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Based on multiple omics and real experimental verification. Environ Toxicol. (2024) 39:869–81. doi: 10.1002/tox.24009 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

