A host E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates Salmonella virulence by targeting an SPI-2 effector involved in SIF biogenesis
- PMID: 38817622
- PMCID: PMC10989757
- DOI: 10.1002/mlf2.12063
A host E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates Salmonella virulence by targeting an SPI-2 effector involved in SIF biogenesis
Abstract
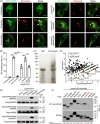
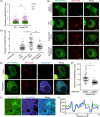
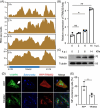
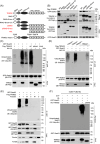
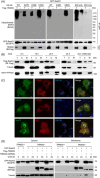
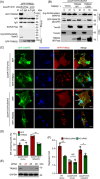
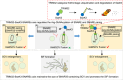
Salmonella Typhimurium creates an intracellular niche for its replication by utilizing a large cohort of effectors, including several that function to interfere with host ubiquitin signaling. Although the mechanism of action of many such effectors has been elucidated, how the interplay between the host ubiquitin network and bacterial virulence factors dictates the outcome of infection largely remains undefined. In this study, we found that the SPI-2 effector SseK3 inhibits SNARE pairing to promote the formation of a Salmonella-induced filament by Arg-GlcNAcylation of SNARE proteins, including SNAP25, VAMP8, and Syntaxin. Further study reveals that host cells counteract the activity of SseK3 by inducing the expression of the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM32, which catalyzes K48-linked ubiquitination on SseK3 and targets its membrane-associated portion for degradation. Hence, TRIM32 antagonizes SNAP25 Arg-GlcNAcylation induced by SseK3 to restrict Salmonella-induced filament biogenesis and Salmonella replication. Our study reveals a mechanism by which host cells inhibit bacterial replication by eliminating specific virulence factors.
Keywords: E3 ligase; SIF biogenesis; Salmonella; T3SS SPI‐2 effector.
© 2023 The Authors. mLife published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SseK3 Is a Salmonella Effector That Binds TRIM32 and Modulates the Host's NF-κB Signalling Activity.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 22;10(9):e0138529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138529. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26394407 Free PMC article.
-
SseK1 and SseK3 Type III Secretion System Effectors Inhibit NF-κB Signaling and Necroptotic Cell Death in Salmonella-Infected Macrophages.Infect Immun. 2017 Feb 23;85(3):e00010-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00010-17. Print 2017 Mar. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28069818 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella Effector SteA Suppresses Proinflammatory Responses of the Host by Interfering With IκB Degradation.Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 10;10:2822. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02822. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31921113 Free PMC article.
-
The exploitation of host autophagy and ubiquitin machinery by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in shaping immune responses and host defense during infection.Autophagy. 2023 Jan;19(1):3-23. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.2021495. Epub 2022 Jan 9. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 35000542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of host cell death in Salmonella infections.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;289:131-50. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27320-4_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15791954 Review.
Cited by
-
An E3 ligase TRIM1 promotes colorectal cancer progression via K63-linked ubiquitination and activation of HIF1α.Oncogenesis. 2024 May 20;13(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s41389-024-00517-2. Oncogenesis. 2024. PMID: 38769340 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Patho-Genomics of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Reveal Potential Host-Specific Virulence Factors.Pathogens. 2025 Feb 1;14(2):128. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14020128. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40005504 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between Salmonella and host: Mechanisms and strategies for bacterial survival.Cell Insight. 2025 Feb 13;4(2):100237. doi: 10.1016/j.cellin.2025.100237. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cell Insight. 2025. PMID: 40177681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Speaking the host language: how Salmonella effector proteins manipulate the host.Microbiology (Reading). 2023 Jun;169(6):001342. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001342. Microbiology (Reading). 2023. PMID: 37279149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acheson D, Hohmann EL. Nontyphoidal salmonellosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:263–9. - PubMed
-
- Dos Santos AMP, Ferrari RG, Conte‐Junior CA. Type three secretion system in Salmonella Typhimurium: the key to infection. Genes Genom. 2020;42:495–506. - PubMed
-
- Jennings E, Thurston TLM, Holden DW. Salmonella SPI‐2 type III secretion system effectors: molecular mechanisms and physiological consequences. Cell Host Microbe. 2017;22:217–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
