Present and future of new systemic therapies for early and intermediate stages of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38817666
- PMCID: PMC11135412
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i19.2512
Present and future of new systemic therapies for early and intermediate stages of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a high mortality neoplasm which usually appears on a cirrhotic liver. The therapeutic arsenal and subsequent prognostic outlook are intrinsically linked to the HCC stage at diagnosis. Notwithstanding the current deployment of treatments with curative intent (liver resection/local ablation and liver transplantation) in early and intermediate stages, a high rate of HCC recurrence persists, underscoring a pivotal clinical challenge. Emergent systemic therapies (ST), particularly immunotherapy, have demonstrate promising outcomes in terms of increase overall survival, but they are currently bound to the advanced stage of HCC. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the literature, encompassing studies up to March 10, 2024, evaluating the impact of novel ST in the early and intermediate HCC stages, specially focusing on the findings of neoadjuvant and adjuvant regimens, aimed at increasing significantly overall survival and recurrence-free survival after a treatment with curative intent. We also investigate the potential role of ST in enhancing the downstaging rate for the intermediate-stage HCC initially deemed ineligible for treatment with curative intent. Finally, we critically discuss about the current relevance of the results of these studies and the encouraging future implications of ST in the treatment schedules of early and intermediate HCC stages.
Keywords: Adjuvant; Early stage; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Intermediate stage; Neoadjuvant; Systemic therapy.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Juan Jose Urquijo-Ponce and Moisés Diago have been paid for serving as a speaker and consultant for Roche. The remaining authors disclose no conflicts of interest to declare regarding the topics covered in this manuscript.
Figures
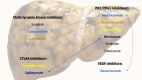
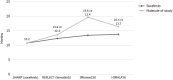
References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I, Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer (2020). [cited 10 November 2023]. Available from: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today/
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Konyn P, Ahmed A, Kim D. Current epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;15:1295–1307. - PubMed
-
- Devarbhavi H, Asrani SK, Arab JP, Nartey YA, Pose E, Kamath PS. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J Hepatol. 2023;79:516–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

