Standardization and Clinical Use of a Single-vial Formulation of Technetium-99m-Trodat Using Autoclave Method
- PMID: 38817725
- PMCID: PMC11135367
- DOI: 10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_104_23
Standardization and Clinical Use of a Single-vial Formulation of Technetium-99m-Trodat Using Autoclave Method
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. SPECT imaging using technetium-99m [99mTc] labeled trodat is the choice of imaging to differentiate PD from its other forms like drug-induced PD.
Aims and objectives: The main objective of our study was to prepare in-house sterile formulation of [99mTc]Tc-trodat and use in clinics.
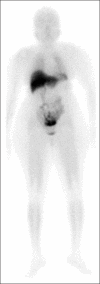
Materials and methods: The labeling of trodat was standardized using glucoheptonate sodium salt (GHA), stannous chloride dihydrate (in 0.05 N HCl), and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Na-EDTA). The preparation was mixed and autoclaved at 15 psi for 15 min. The standardised formulation was stored at 4°C, -20°C and -80°C and labeling with 99mTc was tested for up to 6 days. The radiochemical purity, chemical impurities, and endotoxin levels were tested. The frozen formulation was tested in swiss mice (n = 3) for biodistribution studies at 4 h. Around 18 ± 2 mCi was injected intravenously in each patient (n = 5) and the image was acquired at 4 h post-injection.
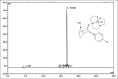
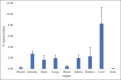
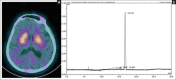
Results: The radiochemical purity of the preparation was 98.3 ± 1.4% with a retention time of 16.8 ± 1.5 min as compared to 4.0 ± 0.5 min for free 99mTc. Animal distribution showed highest uptake in liver and dual excretion via hepatobiliary and renal system. [99mTc]Tc-trodat imaging was able to differentiate both caudate and putamen.
Conclusions: In-house frozen preparation was advantageous, as it has decreased the chance of manual error as compared to daily make up formulations and economical as compared to commercially available kits.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; single-photon emission computed photography; technetium-99m; trodat.
Copyright: © 2024 Indian Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An improved kit formulation of a dopamine transporter imaging agent: [Tc-99m]TRODAT-1.Nucl Med Biol. 1999 May;26(4):461-6. doi: 10.1016/s0969-8051(99)00010-4. Nucl Med Biol. 1999. PMID: 10382851
-
In-house Preparation and Quality Control of Tc99m TRODAT 1 for Diagnostic Single-photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography Imaging in Parkinson's Disease.Indian J Nucl Med. 2017 Oct-Dec;32(4):266-270. doi: 10.4103/ijnm.IJNM_111_17. Indian J Nucl Med. 2017. PMID: 29142341 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 99mTc-TRODAT-1 SPECT and 18 F-AV-133 PET imaging in healthy controls and Parkinson's disease patients.Nucl Med Biol. 2014 Apr;41(4):322-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2013.12.017. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Nucl Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24503330
-
Preparation of 99mTc-TRODAT-1 with high labeling yield in boiling water bath: a new formulation.Nucl Med Biol. 2014 Apr;41(4):317-21. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Nucl Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24607434
-
[2[[2-[[[3-(4-chlorophenyl)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3,2,1]-oct-2-yl]-methyl](2-mercaptoethyl)amino]ethyl]amino]ethanethiolato(3-)-N2,N2’,S2,S2]oxo-[1R-exo-exo)])- [99mTc]-technetium.2007 Apr 24 [updated 2007 Dec 20]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2007 Apr 24 [updated 2007 Dec 20]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641907 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
