Role of KDM2B epigenetic factor in regulating calcium signaling in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 38817821
- PMCID: PMC11135025
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102109
Role of KDM2B epigenetic factor in regulating calcium signaling in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
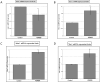
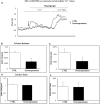
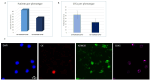
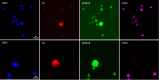
KDM2B, a histone lysine demethylase, is expressed in a plethora of cancers. Earlier studies from our group, have showcased that overexpression of KDM2B in the human prostate cancer cell line DU-145 is associated with cell adhesion, actin reorganization, and improved cancer cell migration. In addition, we have previously examined changes of cytosolic Ca2+, regulated by the pore-forming proteins ORAI and the Ca2+ sensing stromal interaction molecules (STIM), via store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) in wild-type DU-145. This study sought to evaluate the impact of KDM2B overexpression on the expression of key molecules (SGK1, Nhe1, Orai1, Stim1) and SOCE. Furthermore, this is the first study to evaluate KDM2B expression in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from patients with prostate cancer. mRNA levels for SGK1, Nhe1, Orai1, and Stim1 were quantified by RT-PCR. Calcium signals were measured in KDM2B-overexpressing DU-145 cells, loaded with Fura-2. Blood samples from 22 prostate cancer cases were scrutinized for KDM2B expression using immunofluorescence staining and the VyCAP system. KDM2B overexpression in DU-145 cells increased Orai1, Stim1, and Nhe1 mRNA levels and significantly decreased Ca2+ release. KDM2B expression was examined in 22 prostate cancer patients. CTCs were identified in 45 % of these patients. 80 % of the cytokeratin (CK)-positive patients and 63 % of the total examined CTCs exhibited the (CK + KDM2B + CD45-) phenotype. To conclude, this study is the first to report increased expression of KDM2B in CTCs from patients with prostate cancer, bridging in vitro and preclinical assessments on the potentially crucial role of KDM2B on migration, invasiveness, and ultimately metastasis in prostate cancer.
Keywords: Calcium signaling; Circulating tumor cells; KDM2B; Orai1; Prostate cancer; Stim1; Store-operated Ca2+ entry.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
STIM1, ORAI1, and KDM2B in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) isolated from prostate cancer patients.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 5;12:1399092. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1399092. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38903530 Free PMC article.
-
Vasopressin-stimulated ORAI1 expression and store-operated Ca2+ entry in aortic smooth muscle cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Mar;99(3):373-382. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-02016-4. Epub 2021 Jan 7. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33409552
-
To die or not to die SGK1-sensitive ORAI/STIM in cell survival.Cell Calcium. 2018 Sep;74:29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 3. Cell Calcium. 2018. PMID: 29807219 Review.
-
The epigenetic factor KDM2B regulates cell adhesion, small rho GTPases, actin cytoskeleton and migration in prostate cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018 Apr;1865(4):587-597. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29408056
-
The STIM-Orai Pathway: Conformational Coupling Between STIM and Orai in the Activation of Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;993:83-98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-57732-6_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28900910 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

