A miRNA-21-Mediated PTEN/Akt/NF-κB Axis Promotes Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Pathogenesis
- PMID: 38817823
- PMCID: PMC11137736
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S453593
A miRNA-21-Mediated PTEN/Akt/NF-κB Axis Promotes Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Pathogenesis
Abstract
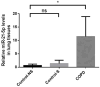
Background: This study sought to explore the underlying mechanism of miR-21 mediated apoptosis and inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) induced by cigarette smoke (CS).
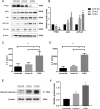
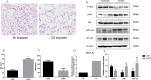
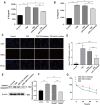
Methods: We detected levels and PTEN/Akt/NF-κB axis protein levels in peripheral lung tissues of COPD patients and CS-exposed mice and HBE cells. Western blotting assay was used to determine the expression of cleaved caspase-3. IL-6 and IL-8 protein was detected in cell supernatant from cells by ELISA. HBE cells were transfected with a miR-21 inhibitor, and co-culture with A549.
Results: Increased miR-21 expression, reduced PTEN expression and following activation of Akt in in peripheral lung tissues of COPD patients and CS-exposed mice and HBE cells. Inhibition of miR-21 showed enhanced PTEN levels and reduced the expression of phosphorylated form of Akt and NF-κB. Decreased expression of cleaved caspase-3, IL-6 and IL-8 in A549 cells co cultured with HBE cells transfected with miR-21 inhibitor compared with transfected with miR-21 control inhibitor.
Conclusion: MiR-21 contributes to COPD pathogenesis by modulating apoptosis and inflammation through the PTEN/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Targeting miR-21 may increase PTEN expression and inhibit Akt/NF-κB pathway, offering potential diagnostic and therapeutic value in COPD management.
Keywords: COPD; PTEN/Akt/NF-κB axis; apoptosis; inflammation; miR-21.
© 2024 Sai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Xiaoyan Sai, Chu Qin, and Zixiao Zhang are co-first authors for this study. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Jul 20;45(7):1409-1422. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.07. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40673303 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
HMGB1-mediated pyroptosis promotes inflammation and contributes to skeletal muscle atrophy induced by cigarette smoke.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 Jul 1;329(1):C325-C340. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.01014.2024. Epub 2025 May 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40445389
-
Upregulation of ARHGAP18 by miR-613 Inhibits Cigarette Smoke Extract-Induced Apoptosis and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Bronchial Epithelial Cells.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Jul 18;20:2525-2537. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S524723. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 40698118 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of long noncoding RNA SNHG6 alleviates cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation by modulating NF-κB signaling.Environ Toxicol. 2024 May;39(5):2634-2641. doi: 10.1002/tox.24132. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Environ Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38205902
-
Computer and mobile technology interventions for self-management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 23;5(5):CD011425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011425.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28535331 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of STAT3 signaling as a shared pathogenic signature in systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and asthma.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07184-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594490 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of Jing Si herbal tea for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a comprehensive investigation from clinical to basic research.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 21;16:1631839. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1631839. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40761394 Free PMC article.
-
An update on the molecular mechanisms underlying the progression of miR-21 in oral cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Mar 1;23(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03732-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40025548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA‑21: A potential therapeutic target in lung cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Aug;67(2):67. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5773. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40641110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorofenidone alleviates cigarette smoke exposure-induced chronic lung injury by targeting ferroptosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):32149. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83998-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738585 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

