Decoding Gastric Cancer: Machine Learning Insights Into the Significance of COMMDs Family in Immunotherapy and Diagnosis
- PMID: 38817875
- PMCID: PMC11134438
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.94360
Decoding Gastric Cancer: Machine Learning Insights Into the Significance of COMMDs Family in Immunotherapy and Diagnosis
Abstract
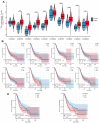
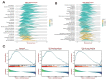
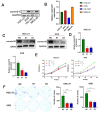
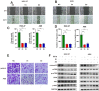
Copper, an indispensable trace element for the human body, serves not only as a crucial auxiliary factor in redox reactions within the organism but also as a significant constituent of numerous key metabolic enzymes. The COMMD family plays a vital role in regulating copper at both the cellular and systemic levels, particularly in the realm of tumor research, an area notably deficient in gastric cancer investigations. With the advancement of precision medical techniques, individualized and precise screening and treatment have become paramount considerations in the contemporary medical landscape for gastric cancer therapy. In light of this, we meticulously scrutinized existing transcriptomic datasets for gastric cancer, validating the expression levels and prognostic value of COMMD family genes. Simultaneously, employing the ssGSEA algorithm, we devised the COMMDs score. Enrichment analysis, gene mutations, and clinical features were incorporated into the assessment of this score. Furthermore, we contextualized the COMMDs score within the framework of the immune microenvironment, evaluating the relationship between the COMMDs family and immune factors as well as immune cells. The results suggest a correlation between the COMMDs score and various immune-related features. Based on this foundation, multiple machine learning approaches indicated Logistic Regression, with a remarkable ROC of 0.972, as the optimal diagnostic model. To accentuate the translational medical value of the COMMDs family, we selected COMMD10 as a differential gene in gastric cancer for further validation. Functional experiments revealed a decline in the proliferative and migratory capabilities of gastric cancer cells upon silencing COMMD10. Additionally, through pathway intervention, we unveiled the PI3K-AKT pathway as a potential mechanism through which COMMD10 influences gastric cancer activity. In summary, our study affirms the prospective role of the COMMDs family as potential markers for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer in the future.
Keywords: COMMDs Family; Gastric Cancer; Immunotherapy; Machine Learning; TME.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Ychou M, Boige V, Pignon JP, Conroy T, Bouche O, Lebreton G. et al. Perioperative chemotherapy compared with surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: an FNCLCC and FFCD multicenter phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1715–21. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura Y, Kawazoe A, Lordick F, Janjigian YY, Shitara K. Biomarker-targeted therapies for advanced-stage gastric and gastro-oesophageal junction cancers: an emerging paradigm. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:473–87. - PubMed
-
- Chao J, Fuchs CS, Shitara K, Tabernero J, Muro K, Van Cutsem E. et al. Assessment of Pembrolizumab Therapy for the Treatment of Microsatellite Instability-High Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer Among Patients in the KEYNOTE-059, KEYNOTE-061, and KEYNOTE-062 Clinical Trials. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:895–902. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

