Eupatilin mitigates Gestational diabetes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic pregnant rats through the Regulation of inflammation and oxidative stress
- PMID: 38818188
- PMCID: PMC11137385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30911
Eupatilin mitigates Gestational diabetes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic pregnant rats through the Regulation of inflammation and oxidative stress
Abstract
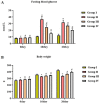
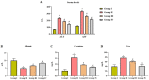
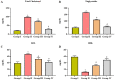
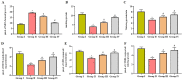
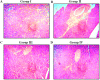
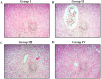
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a common metabolic disease that is typically diagnosed in pregnant women. The current study was aimed at disclosing the salutary activities of eupatilin against streptozotocin (STZ)-induced GDM in rats. The pregnant rats were induced with GDM and then treated with eupatilin for 20 days. The bodyweight, pup numbers and survival, glucose, and insulin levels were estimated. The levels of biochemical markers, antioxidants, and lipid profiles were measured using kits. The histopathological analysis was done on the pancreas and liver tissues. The eupatilin effectively reduced glucose and boosted insulin levels in the GDM rats. The pup numbers and their survival index were increased by the eupatilin treatment. The lipase, creatinine, AST, ALT, and urea levels were effectively reduced by the eupatilin in the GDM rats. Eupatilin treatment also decreased oxidative stress by increasing antioxidant levels and reducing inflammatory cytokine levels in the GDM rats. The cholesterol, LDL, and triglyceride levels were effectively decreased, and HDL was elevated by eupatilin. The results of histopathological analysis of both liver and pancreatic tissues also demonstrated the therapeutic properties of eupatilin. In conclusion, the current results prove that eupatilin can be an effective salutary candidate to treat GDM.
Keywords: Dyslipidemia; Eupatilin; Hyperglycemia; Inflammation; Malondialdehyde.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective effect of sinomenine against inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus in female rats via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Food Biochem. 2021 Nov;45(11):e13952. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13952. Epub 2021 Oct 11. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34636046
-
Myrtenol alleviates oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic pregnant rats via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021 Nov;35(11):e22904. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22904. Epub 2021 Sep 3. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34477272
-
Tert-butylhydroquinone Mitigates Renal Dysfunction in Pregnant Diabetic Rats via Attenuation of Oxidative Stress and Modulation of the iNOs/ NFkB/TNF Alpha Signalling Pathway.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2023;23(5):633-646. doi: 10.2174/1871530322666220908153118. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 36089780
-
Attenuation of hyperglycemia-associated dyslipidemic, oxidative, cognitive, and inflammatory crises via modulation of neuronal ChEs/NF-κB/COX-2/NOx, and hepatorenal functional deficits by the Tridax procumbens extract.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Feb;158:114114. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114114. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36525818
-
Protective effect of nimbolide against streptozotocin induced gestational diabetes mellitus in rats via alteration of inflammatory reaction, oxidative stress, and gut microbiota.Environ Toxicol. 2022 Jun;37(6):1382-1393. doi: 10.1002/tox.23491. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Environ Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35212444
References
-
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee 2 Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical Care in diabete. Dia Care. 2022;45:S17–S38. - PubMed
-
- Shahzad N., Alzahrani A.R., Aziz Ibrahim I.A., Shahid I., Alanazi I.M., Falemban A.H., Imam M.T., Mohsin N., Azlina M.F.N., Arulselvan P. Therapeutic strategy of biological macromolecules based natural bioactive compounds of diabetes mellitus and future perspectives: a systematic review. Heliyon. 2024;10 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

