Current and emerging nanotechnology for sustainable development of agriculture: Implementation design strategy and application
- PMID: 38818209
- PMCID: PMC11137568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31503
Current and emerging nanotechnology for sustainable development of agriculture: Implementation design strategy and application
Abstract
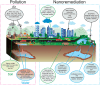
Recently, agriculture systems have faced numerous challenges involving sustainable nutrient use efficiency and feeding, environmental pollution especially heavy metals (HMs), infection of harmful microorganisms, and maintenance of crop production quality during postharvesting and packaging. Nanotechnology and nanomaterials have emerged as powerful tools in agriculture applications that provide alternatives or support traditional methods. This review aims to address and highlight the current overarching issue and various implementation strategies of nanotechnology for sustainable agriculture development. In particular, the current progress of different nano-fertilizers (NFs) systems was analyzed to show their advances in enhancing the uptake and translocations in plants and improving nutrient bioavailability in soil. Also, the design strategy and application of nanotechnology for rapid detection of HMs and pathogenic diseases in plant crops were emphasized. The engineered nanomaterials have great potential for biosensors with high sensitivity and selectivity, high signal throughput, and reproducibility through various detection approaches such as Raman, colorimetric, biological, chemical, and electrical sensors. We obtain that the development of microfluidic and lab-on-a-chip (LoC) technologies offers the opportunity to create on-site portable and smart biodevices and chips for real-time monitoring of plant diseases. The last part of this work is a brief introduction to trends in nanotechnology for harvesting and packaging to provide insights into the overall applications of nanotechnology for crop production quality. This review provides the current advent of nanotechnology in agriculture, which is essential for further studies examining novel applications for sustainable agriculture.
Keywords: Anti-microbial nanomaterials; Heavy metals; Nano-fertilizers; Plant disease; Sustainable agriculture.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Çakmakçı R., Salık M.A., Çakmakçı S. Assessment and principles of environmentally sustainable food and agriculture systems. Agriculture. 2023;13:1073. doi: 10.3390/AGRICULTURE13051073. 2023;13:1073. - DOI
-
- Duro J.A., Lauk C., Kastner T., Erb K.H., Haberl H. Global inequalities in food consumption, cropland demand and land-use efficiency: a decomposition analysis. Global Environ. Change. 2020;64 doi: 10.1016/J.GLOENVCHA.2020.102124. - DOI
-
- Mandal A., Sarkar B., Mandal S., Vithanage M., Patra A.K., Manna M.C. Impact of agrochemicals on soil health. Agrochemicals Detection, Treatment and Remediation: Pesticides and Chemical Fertilizers. 2020:161–187. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-08-103017-2.00007-6. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

