Nano-revolution in hepatocellular carcinoma: A multidisciplinary odyssey - Are we there yet?
- PMID: 38818296
- PMCID: PMC11135275
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i5.684
Nano-revolution in hepatocellular carcinoma: A multidisciplinary odyssey - Are we there yet?
Abstract
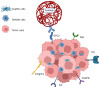
In this editorial we comment on the review by Zhou et al reviewing the landscape of nanomedicine in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We focus on the immense potential of nanotechnology, particularly ligand-receptor mediated nanotherapy, in revolutionizing the treatment landscape of HCC. Despite advancements in multidisciplinary treatment, HCC remains a significant global health challenge. Ligand-mediated nanotherapy offers the opportunity for precise drug delivery to tumor sites, targeting specific receptors overexpressed in HCC cells, thereby enhancing efficacy and minimizing side effects. Overcoming drug resistance and aggressive tumor biology is facilitated by nanomedicine, bypassing traditional hurdles encountered in chemotherapy. Examples include targeting glypican-3, asialoglycoprotein, transferrin receptor or folic acid receptors, capitalizing on their over-expression in tumor cells. The ability for multi-receptor targeting through dual-ligand nanoparticle modification holds the prospect of further enhancement in specificity and efficacy of directed therapy. However, challenges including immune responses, reproducibility in nanoparticle synthesis, and production scalability remain. Future directions involve refining targeting strategies, improving drug release mechanisms, and streamlining production processes to enable personalized and multifunctional nanotherapies. Overall, the integration of nanotherapy in HCC treatment holds immense promise, but continued partnership and effort are needed in offering hope for more effective, precise, and accessible clinical care in the management of HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Ligand-receptor mediated nanotherapy; Nanomedicine; Personalized medicine; Precision medicine; Targeting.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Precision targeting in hepatocellular carcinoma: Exploring ligand-receptor mediated nanotherapy.World J Hepatol. 2024 Feb 27;16(2):164-176. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i2.164. World J Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38495282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promoting Early Diagnosis and Precise Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Glypican-3-Targeted Synergistic Chemo-Photothermal Theranostics.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Jul 3;11(26):23591-23604. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b05526. Epub 2019 Jun 19. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 31179679
-
Advances of Nanotechnology in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 31;12(21):6867. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216867. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37959332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine revolutionizes epilepsy treatment: overcoming therapeutic hurdles with nanoscale solutions.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2024 May;21(5):735-750. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2024.2360528. Epub 2024 May 26. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 38787859 Review.
-
Facile Fabrication of Nanoparticles with Dual-Targeting Ligands for Precise Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy In Vitro and In Vivo.Mol Pharm. 2020 Sep 8;17(9):3223-3235. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00327. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32658485
Cited by
-
Herbal Medicine: Enhancing the Anticancer Potential of Natural Products in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy Through Advanced Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 20;17(5):673. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050673. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40430962 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

