Adaptive time modulation technique for multiplexed on-chip particle detection across scales
- PMID: 38818330
- PMCID: PMC11138143
- DOI: 10.1364/optica.489068
Adaptive time modulation technique for multiplexed on-chip particle detection across scales
Abstract
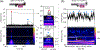
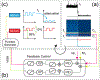
Integrated optofluidic biosensors have demonstrated ultrasensitivity down to single particle detection and attomolar target concentrations. However, a wide dynamic range is highly desirable in practice and can usually only be achieved by using multiple detection modalities or sacrificing linearity. Here, we demonstrate an analysis technique that uses temporal excitation at two different time scales to simultaneously enable digital and analog detection of fluorescent targets. We demonstrated the seamless detection of nanobeads across eight orders of magnitude from attomolar to nanomolar concentration. Furthermore, a combination of spectrally varying modulation frequencies and a closed-loop feedback system that provides rapid adjustment of excitation laser powers enables multiplex analysis in the presence of vastly different concentrations. We demonstrated this ability to detect across scales via an analysis of a mixture of fluorescent nanobeads at femtomolar and picomolar concentrations. This technique advances the performance and versatility of integrated biosensors, especially toward point-of-use applications.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures. Authors Aaron R. Hawkins and Holger Schmidt had a competing interest in Fluxus Inc., which commercializes optofluidic technology. Author Vahid Ganjalizadeh has no competing interests.
Figures
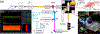

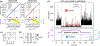
References
-
- Towner JS, Rollin PE, Bausch DG, Sanchez A, Crary SM, Vincent M, Lee WF, Spiropoulou CF, Ksiazek TG, Lukwiya M, Kaducu F, Downing R, and Nichol ST, “Rapid diagnosis of Ebola hemorrhagic fever by reverse transcription-PCR in an outbreak setting and assessment of patient viral load as a predictor of outcome,” J. Virol. 78, 4330–4341 (2004). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kemal Yetisen A, Safwan Akram M, and Lowe CR, “Paper-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices,” Lab Chip 13, 2210–2251 (2013). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
