Regulation of RNase E during the UV stress response in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
- PMID: 38818332
- PMCID: PMC10989929
- DOI: 10.1002/mlf2.12056
Regulation of RNase E during the UV stress response in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Abstract
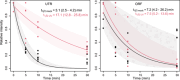
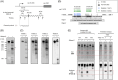
Endoribonucleases govern the maturation and degradation of RNA and are indispensable in the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression. A key endoribonuclease in Gram-negative bacteria is RNase E. To ensure an appropriate supply of RNase E, some bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, feedback-regulate RNase E expression via the rne 5'-untranslated region (5' UTR) in cis. However, the mechanisms involved in the control of RNase E in other bacteria largely remain unknown. Cyanobacteria rely on solar light as an energy source for photosynthesis, despite the inherent ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. In this study, we first investigated globally the changes in gene expression in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 after a brief exposure to UV. Among the 407 responding genes 2 h after UV exposure was a prominent upregulation of rne mRNA level. Moreover, the enzymatic activity of RNase E rapidly increased as well, although the protein stability decreased. This unique response was underpinned by the increased accumulation of full-length rne mRNA caused by the stabilization of its 5' UTR and suppression of premature transcriptional termination, but not by an increased transcription rate. Mapping of RNA 3' ends and in vitro cleavage assays revealed that RNase E cleaves within a stretch of six consecutive uridine residues within the rne 5' UTR, indicating autoregulation. These observations suggest that RNase E in cyanobacteria contributes to reshaping the transcriptome during the UV stress response and that its required activity level is secured at the RNA level despite the enhanced turnover of the protein.
Keywords: cyanobacteria; protein turnover; ribonuclease; stress response.
© 2023 The Authors. mLife published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures





References
-
- Coburn GA, Mackie GA. Degradation of mRNA in Escherichia coli: an old problem with some new twists. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1999;62:55–108. - PubMed
-
- Mackie GA. RNase E: at the interface of bacterial RNA processing and decay. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:45–57. - PubMed
-
- Ehretsmann CP, Carpousis AJ, Krisch HM. Specificity of Escherichia coli endoribonuclease RNase E: in vivo and in vitro analysis of mutants in a bacteriophage T4 mRNA processing site. Genes Dev. 1992;6:149–59. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
