The Effect of Pregabalin on Microglia Differentiation in Rat with Neuropathic pain: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 38818478
- PMCID: PMC11134577
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.96236
The Effect of Pregabalin on Microglia Differentiation in Rat with Neuropathic pain: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
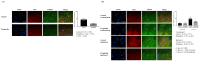
This study investigated the effects of pregabalin on microglial differentiation in rats with neuropathic pain (NP) induced by sciatic nerve ligation and transection. After confirming NP, the rats were randomly allocated to either a pregabalin or control group. The pregabalin group received intraperitoneal injections of 10 mg/kg pregabalin, while the control group received an equivalent volume of normal saline following surgery. On postoperative day 28, neuronal damage, microglial activity, and microglial differentiation were assessed. The pregabalin group exhibited significantly less neuronal damage compared to the control group, along with a significant decrease in activated microglial expression in both the brain and spinal cord. Pregabalin treatment also significantly altered the microglial phenotype expression, with a decrease in the M1 phenotype percentage and an increase in the M2 phenotype percentage in both the brain (M1 phenotype: 43.52 ± 12.16% and 18.00 ± 8.57% in the control and pregabalin groups, respectively; difference: 27.26 [15.18-42.10], p = 0.002; M2 phenotype: 16.88 ± 6.47% and 39.63 ± 5.82% in the control and pregabalin groups, respectively; difference 22.04 [17.17-32.70], p < 0.001) and the spinal cord ipsilateral to nerve injury (M1 phenotype: 44.35 ± 12.12% and 13.78 ± 5.39% in the control and pregabalin groups, respectively; difference 30.46 [21.73-44.45], p < 0.001; M2 phenotype: 7.64 ± 3.91% and 33.66 ± 7.95% in the control and pregabalin groups, respectively; difference 27.41 [21.21-36.30], p < 0.001). Overall, pregabalin treatment significantly decreased the microglial M1 phenotype while increasing the microglial M2 phenotype in NP rats.
Keywords: Allodynia; Cytokine; Microglia; Neuropathic pain; Pregabalin.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

 ) Contralateral side for the surgery, Control group, (
) Contralateral side for the surgery, Control group, ( ) Contralateral side for the surgery, Pregabalin group, (
) Contralateral side for the surgery, Pregabalin group, ( ) Ipsilateral side for the surgery, Control group, (
) Ipsilateral side for the surgery, Control group, ( ) Ipsilateral side for the surgery, Pregabalin group. Abbreviations: Control, Control group; Pregabalin, Pregabalin group; D0, before the surgery; D, day after the surgery; before, before the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin; after, 60 minutes after the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin. *p < 0.05 compared with D0 in intra-group variance. †p < 0.05 compared with Control group.
) Ipsilateral side for the surgery, Pregabalin group. Abbreviations: Control, Control group; Pregabalin, Pregabalin group; D0, before the surgery; D, day after the surgery; before, before the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin; after, 60 minutes after the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin. *p < 0.05 compared with D0 in intra-group variance. †p < 0.05 compared with Control group.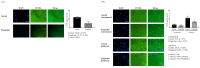

Similar articles
-
Effect of Microglial Activity on Gut Microbiota in Rats with Neuropathic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5181. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115181. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507989 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Pain Sensitivity with Systemic Ultrastructural Changes of the Nervous Systems after Cobra Venom Injection is Reversed by Electroacupuncture Treatment.Pain Physician. 2018 Sep;21(5):E509-E521. Pain Physician. 2018. PMID: 30282399
-
Minocycline modulates neuropathic pain behaviour and cortical M1-M2 microglial gene expression in a rat model of depression.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Nov;42:147-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.06.015. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24994592
-
Interventions for treating neuropathic pain in people with sickle cell disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jul 5;7(7):CD012943. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012943.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31273755 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in the Spinal Microglia Serve Critical Roles in Neuropathic Pain.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Jan;58(1):132-142. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02102-1. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32902792 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Microglial Activity on Gut Microbiota in Rats with Neuropathic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5181. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115181. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jensen TS, Finnerup NB. Allodynia and hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain: clinical manifestations and mechanisms. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:924–35. - PubMed
-
- Bouhassira D, Attal N. Personalized treatment of neuropathic pain: Where are we now? Eur J Pain. 2023;27:1084–98. - PubMed
-
- Fehrenbacher JC, Taylor CP, Vasko MR. Pregabalin and gabapentin reduce release of substance P and CGRP from rat spinal tissues only after inflammation or activation of protein kinase C. Pain. 2003;105:133–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

