Zhi-zi-chi decoction mitigates depression by enhancing lncRNA Six3os1 expression and promoting histone H3K4 methylation at the BDNF promoter
- PMID: 38818577
- PMCID: PMC11140235
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18365
Zhi-zi-chi decoction mitigates depression by enhancing lncRNA Six3os1 expression and promoting histone H3K4 methylation at the BDNF promoter
Abstract
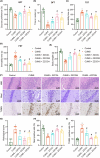
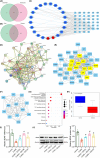
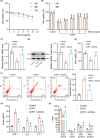
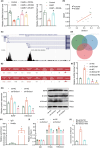
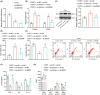
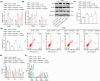
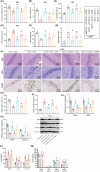
Traditional Chinese medicine, particularly Zhi-zi-chi decoction (ZZCD), is gaining recognition as a potential treatment for depression. This study aimed to uncover the molecular mechanisms behind ZZCD's antidepressant effects, focusing on lncRNA Six3os1 and histone H3K4 methylation at the BDNF promoter. Network pharmacology and in vivo experiments were conducted to identify ZZCD targets and evaluate its impact on depression-related behaviours and neuron injury. The role of Six3os1 in recruiting KMT2A to the BDNF promoter and its effects on oxidative stress and neuron injury were investigated. ZZCD reduced depression-like behaviours and neuron injury in mice subjected to chronic stress. It upregulated Six3os1, which facilitated KMT2A recruitment to the BDNF promoter, leading to increased histone H3K4 methylation and enhanced BDNF expression. ZZCD also inhibited CORT-induced neuron injury, inflammatory response and oxidative stress in vitro. ZZCD's antidepressant properties involve Six3os1 upregulation, which exerts neuroprotective effects by inhibiting oxidative stress and neuron injury, thereby alleviating depressive symptoms. Targeting Six3os1 upregulation may offer a potential therapeutic intervention for depression.
Keywords: BDNF; KMT2A; LncRNA Six3os1; Zhi‐zi‐chi decoction; anti‐depressive mechanism; histone methylation; neuron injury; traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zhi-Zi-Chi decoction ameliorates depression-like behavior in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced mice via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jun 26;350:119987. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119987. Epub 2025 May 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40403895
-
Anti-depressant effect of Zhi-zi-chi decoction on CUMS mice and elucidation of its signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;266:113283. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113283. Epub 2020 Aug 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32827659
-
Geniposide improves depression by promoting the expression of synapse-related proteins through the Creb1/Six3os1 axis.Gene. 2023 Aug 15;877:147564. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147564. Epub 2023 Jun 11. Gene. 2023. PMID: 37311497
-
Therapeutic potential of plant iridoids in depression: a review.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):2167-2181. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2136206. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 36300881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF - a key transducer of antidepressant effects.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Mar;102:72-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.10.034. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26519901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morinda officinalis oligosaccharides alleviate chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression through the BDNF/TrkB/CREB pathway and symptoms of sexual dysfunction in mice.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jan 8;18:1509543. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1509543. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39844852 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic preconditioning modulates BDNF signaling to alleviate depression-like behaviors in mice and its whole transcriptome sequencing analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 May 2;15(1):15363. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00355-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40316595 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the LINC00641/miR-323a-3p/EIF4G2 axis on behaviors and brain monoamine neurotransmitters in chronic unpredictable mild stress mice.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Apr 28;41(1):76. doi: 10.1007/s10565-025-10015-9. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40293545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mccarron RM, Shapiro B, Rawles J, Luo J. Depression. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(5):ITC65‐ITC80. - PubMed
-
- Suseelan S, Pinna G. Heterogeneity in major depressive disorder: the need for biomarker‐based personalized treatments. Adv Clin Chem. 2023;112:1‐67. - PubMed
-
- Miller RL, Grayson MH, Strothman K. Advances in asthma: new understandings of asthma's natural history, risk factors, underlying mechanisms, and clinical management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148(6):1430‐1441. - PubMed
-
- Marx W, Lane M, Hockey M, et al. Diet and depression: exploring the biological mechanisms of action. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(1):134‐150. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

