LARP7 overexpression alleviates aortic senescence and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 38818612
- PMCID: PMC11140237
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18388
LARP7 overexpression alleviates aortic senescence and atherosclerosis
Abstract
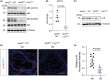
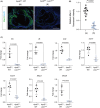
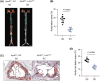
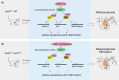
Atherosclerosis, characterized by the accumulation of lipid plaques on the inner walls of arteries, is the leading cause of heart attack, stroke and severe ischemic injuries. Senescent cells have been found to accumulate within atherosclerotic lesions and contribute to the progression of atherosclerosis. In our previous study, we discovered that suppressing Larp7 accelerates senescence by inhibiting Sirt1 activity, resulting in increased atherosclerosis in high-fat diet (HFD) fed and ApoE deficient (ApoEKO) mice. However, there has been no direct evidence demonstrating Larp7 per se could attenuate atherosclerosis. To this end, we generated a tetO-controlled and Cre-activated Larp7 gain-of-function mouse. Through RT-PCR and western blotting, we confirmed Larp7 overexpression in the aortas of HFD-fed ApoEKO; Larp7tetO mice. Larp7 overexpression led to increased Sirt1 activity and decreased cellular senescence signals mediated by p53/p65 in the aortas. Additionally, Larp7 overexpression reduced the presence of p16-positive senescent cells in the aortic lesions. Furthermore, Larp7 overexpression resulted in a decrease in pro-inflammatory macrophages and SASP factors. Consequently, Larp7 overexpression led to a reduction in the area of atherosclerotic lesions in HFD-fed ApoEKO; Larp7tetO mice. In summary, our study provides evidence that Larp7 overexpression holds promise as an approach to inhibit cellular senescence and prevent atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Larp7; Sirt1; atherosclerosis; cellular senescence.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
LARP7 ameliorates cellular senescence and aging by allosterically enhancing SIRT1 deacetylase activity.Cell Rep. 2021 Nov 23;37(8):110038. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110038. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34818543
-
Fibronectin Splicing Variants Containing Extra Domain A Promote Atherosclerosis in Mice Through Toll-Like Receptor 4.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Nov;35(11):2391-400. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306474. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26427793 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1 overexpression exacerbates atherosclerosis and induces aortic aneurysms in apolipoprotein E knockout mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Oct;33(10):2306-15. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302028. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23887640
-
SIRT1 mediates the inflammatory response of macrophages and regulates the TIMP3/ADAM17 pathway in atherosclerosis.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Oct 1;442(2):114253. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114253. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 39271099
-
Assessment and consequences of cell senescence in atherosclerosis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2016 Oct;27(5):431-8. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000327. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2016. PMID: 27261931 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021-01-07-00-02-E00088/Innovation Program of the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission
- 21dz2210200/WLA Program of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission
- 21dz2210202/WLA Program of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission
- 21X010500929/Startup Fund for Young Faculty of SJTU
- 2020YFA0803800/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2020YFA0803802/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2023YFA1800700/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2023YFA1800702/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 82225006/National Foundation of Distinguished Young Scholar of China
- YG2021ZD11/SJTU STAR Award
- YG2022ZD023/SJTU STAR Award
- 81901515/Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

