Detection accuracy and clinical applications of DP-TOF mass spectrometry
- PMID: 38819085
- PMCID: PMC11143829
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605241255568
Detection accuracy and clinical applications of DP-TOF mass spectrometry
Abstract
Objective: Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) is currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories. This study aimed to determine whether dual-polarity time-of-flight mass spectrometry (DP-TOF MS) could be applied to clinical nucleotide detection.
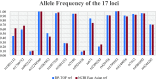
Methods: This prospective study included 40 healthy individuals and 110 patients diagnosed with cardiovascular diseases. We used DP-TOF MS and Sanger sequencing to evaluate 17 loci across 11 genes associated with cardiovascular drug responses. In addition, we used DP-TOF MS to test 998 retrospectively collected clinical DNA samples with known results.
Results: A, T, and G nucleotide detection by DP-TOF MS and Sanger sequencing revealed 100% concordance, whereas the C nucleotide concordance was 99.86%. Genotyping based on the results of the two methods showed 99.96% concordance. Regarding clinical applications, DP-TOF MS yielded a 99.91% concordance rate for known loci. The minimum detection limit for DNA was 0.4 ng; the inter-assay and intra-assay precision rates were both 100%. Anti-interference analysis showed that aerosol contamination greater than 1013 copies/µL in the laboratory environment could influence the results of DP-TOF MS.
Conclusions: The DP-TOF MS platform displayed good detection performance, as demonstrated by its 99.96% concordance rate with Sanger sequencing. Thus, it may be applied to clinical nucleotide detection.
Keywords: Time-of-flight mass spectrometry; cardiovascular disease; drug response-associated gene; molecular diagnostics; multigene detection; nucleotide detection; personalized medicine; pharmacogenetics; precision medicine; verification.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aebersold R, Mann M. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 2003; 422: 198–207. doi: 10.1038/nature01511. - PubMed
-
- Király M, Dalmadiné Kiss B, Vékey K, et al.. Mass spectrometry: past and present. Acta Pharm Hung 2016; 86: 3–11. - PubMed
-
- Matthiesen R, Bunkenborg J. Introduction to mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Methods Mol Biol 2013; 1007: 1–45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-392-3_1. - PubMed
-
- Eliuk S, Makarov A. Evolution of Orbitrap mass spectrometry instrumentation. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif) 2015; 8: 61–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-071114-040325. - PubMed
-
- Singhal N, Kumar M, Virdi JS. MALDI-TOF MS in clinical parasitology: applications, constraints and prospects. Parasitology 2016; 143: 1491–1500. doi: 10.1017/s0031182016001189. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources