Oral Estrogen Receptor PROTAC Vepdegestrant (ARV-471) Is Highly Efficacious as Monotherapy and in Combination with CDK4/6 or PI3K/mTOR Pathway Inhibitors in Preclinical ER+ Breast Cancer Models
- PMID: 38819400
- PMCID: PMC11325148
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3465
Oral Estrogen Receptor PROTAC Vepdegestrant (ARV-471) Is Highly Efficacious as Monotherapy and in Combination with CDK4/6 or PI3K/mTOR Pathway Inhibitors in Preclinical ER+ Breast Cancer Models
Abstract
Purpose: Estrogen receptor (ER) alpha signaling is a known driver of ER-positive (ER+)/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative (HER2-) breast cancer. Combining endocrine therapy (ET) such as fulvestrant with CDK4/6, mTOR, or PI3K inhibitors has become a central strategy in the treatment of ER+ advanced breast cancer. However, suboptimal ER inhibition and resistance resulting from the ESR1 mutation dictates that new therapies are needed.
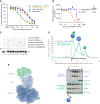
Experimental design: A medicinal chemistry campaign identified vepdegestrant (ARV-471), a selective, orally bioavailable, and potent small molecule PROteolysis-TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) degrader of ER. We used biochemical and intracellular target engagement assays to demonstrate the mechanism of action of vepdegestrant, and ESR1 wild-type (WT) and mutant ER+ preclinical breast cancer models to demonstrate ER degradation-mediated tumor growth inhibition (TGI).
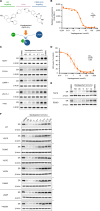
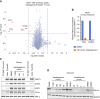
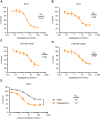
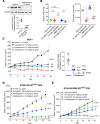
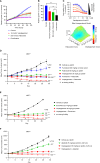
Results: Vepdegestrant induced ≥90% degradation of wild-type and mutant ER, inhibited ER-dependent breast cancer cell line proliferation in vitro, and achieved substantial TGI (87%-123%) in MCF7 orthotopic xenograft models, better than those of the ET agent fulvestrant (31%-80% TGI). In the hormone independent (HI) mutant ER Y537S patient-derived xenograft (PDX) breast cancer model ST941/HI, vepdegestrant achieved tumor regression and was similarly efficacious in the ST941/HI/PBR palbociclib-resistant model (102% TGI). Vepdegestrant-induced robust tumor regressions in combination with each of the CDK4/6 inhibitors palbociclib, abemaciclib, and ribociclib; the mTOR inhibitor everolimus; and the PI3K inhibitors alpelisib and inavolisib.
Conclusions: Vepdegestrant achieved greater ER degradation in vivo compared with fulvestrant, which correlated with improved TGI, suggesting vepdegestrant could be a more effective backbone ET for patients with ER+/HER2- breast cancer.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
S.M. Gough reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, as well as patents for PCTUS2020047693, PCTUS2021063130, PCTUS2023031574, and PCTUS202331568 issued; in addition, S.M. Gough is an Arvinas shareholder. J.J. Flanagan reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, as well as patents for PCTUS2020047693, PCTUS2021063130, PCTUS2023031574, and PCTUS202331568 issued; in addition, J.J. Flanagan is an Arvinas shareholder, and is currently employed by Tasca Therapeutics. J. Teh reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, as well as patents for PCTUS24014593 and PCTUS2024021150 pending, and a patent for US11571483B2 issued; in addition, J. Teh is an Arvinas shareholder. M. Andreoli reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. E. Rousseau reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. M. Pannone reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is currently employed by Chroma Medicine. M. Bookbinder reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. R. Willard reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, is an Arvinas shareholder, and is currently employed by Kolm Therapeutics. K. Davenport reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. E. Bortolon reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. G. Cadelina reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. D. Gordon reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. J. Pizzano reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. J. Macaluso reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is currently employed by Boehringer Ingelheim. L. Soto reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. J. Corradi reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. K. Digianantonio reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. I. Drulyte reports other support from Thermo Fisher Scientific outside the submitted work, and is a Thermo Fisher Scientific shareholder. A. Morgan reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. C. Quinn reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. M. Békés reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. C. Ferraro reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. X. Chen reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, as well as patents for PCTUS2020047693 and PCTUS2021063130 issued; in addition, X. Chen is an Arvinas shareholder. G. Wang reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. H. Dong reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, as well as patents for PCTUS2017064283 and PCTUS22038343 issued; in addition, H. Dong is an Arvinas shareholder. J. Wang reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, as well as patents for PCTUS2017064283, PCTUS2020047693, and PCTUS2021063130 issued; in addition, J. Wang is an Arvinas shareholder. D.R. Langley reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. J. Houston reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, and is an Arvinas shareholder. R. Gedrich reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, as well as patents for PCTUS24014593 and PCTUS2024021150 pending and was an Arvinas shareholder at the time work was performed; in addition, R. Gedrich is currently employed by PIC Therapeutics. I.C. Taylor reports other support from Arvinas outside the submitted work, as well as patents for PCTUS2020047693, PCTUS2021063130, PCTUS2023031574, and PCTUS202331568 issued, and a patent for PCTUS2024021150 pending; in addition, I.C. Taylor is an Arvinas shareholder.
Figures
References
-
- Neklesa TK, Winkler JD, Crews CM. Targeted protein degradation by PROTACs. Pharmacol Ther 2017;174:138–44. - PubMed
-
- Snyder LB, Neklesa TK, Chen X, Dong H, Ferraro C, Gordon DA, et al. Abstract 43: discovery of ARV-110, a first in class androgen receptor degrading PROTAC for the treatment of men with metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2021;81:43.
-
- Snyder LB, Flanagan JJ, Qian Y, Gough SM, Andreoli M, Bookbinder M, et al. Abstract 44: the discovery of ARV-471, an orally bioavailable estrogen receptor degrading PROTAC for the treatment of patients with breast cancer. Cancer Res 2021;81:44.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

