Polyneuropathy Unveiling a Hidden Hepatic Plasmacytoma: An Extremely Rare Association
- PMID: 38819414
- PMCID: PMC11418771
- DOI: 10.4103/aian.aian_28_24
Polyneuropathy Unveiling a Hidden Hepatic Plasmacytoma: An Extremely Rare Association
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
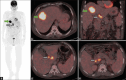
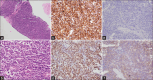
Similar articles
-
Adenopathy and extensive skin patch overlying plasmacytoma syndrome-the clue to early diagnosis of polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, and skin changes: A case series and literature review.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2022 Apr 25;10:2050313X221091602. doi: 10.1177/2050313X221091602. eCollection 2022. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35495293 Free PMC article.
-
Solitary osteosclerotic plasmacytoma: association with demyelinating polyneuropathy and amyloid deposition.Skeletal Radiol. 2001 Sep;30(9):527-9. doi: 10.1007/s002560100391. Skeletal Radiol. 2001. PMID: 11587522
-
[Chronic demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy revealing a solitary plasmacytoma of the right iliac bone].Rev Med Liege. 2017 Jul;72(7-8):377-379. Rev Med Liege. 2017. PMID: 28795553 French.
-
Adenopathy and extensive skin patch overlying a plasmacytoma with unusual histologic findings in a patient with polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal protein and skin changes syndrome and Castleman disease.J Cutan Pathol. 2019 Oct;46(10):784-789. doi: 10.1111/cup.13514. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Cutan Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31119772 Review.
-
The AESOP (adenopathy and extensive skin patch overlying a plasmacytoma) syndrome: report of 4 cases of a new syndrome revealing POEMS (polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal protein, and skin changes) syndrome at a curable stage.Medicine (Baltimore). 2003 Jan;82(1):51-9. doi: 10.1097/00005792-200301000-00005. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003. PMID: 12544710 Review.
References
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Hamilos G. Solitary bone plasmacytoma and extramedullary plasmacytoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2002;3:255–9. - PubMed
-
- Husaric S, Pasic J, Alic E, Kuljanin M. Solitary extramedullary plasmacytoma of the liver. Acta Med Acad. 2013;42:85–6. - PubMed
-
- Bladé J, Fernández de Larrea C, Rosiñol L, Cibeira MT, Jiménez R, Powles R. Soft-tissue plasmacytomas in multiple myeloma: Incidence, mechanisms of extramedullary spread, and treatment approach. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3805–12. - PubMed
-
- Finsinger P, Grammatico S, Chisini M, Piciocchi A, Foà R, Petrucci MT. Clinical features and prognostic factors in solitary plasmacytoma. Br J Haematol. 2016;172:554–60. - PubMed

