THY1 is a prognostic-related biomarker via mediating immune infiltration in lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC)
- PMID: 38819947
- PMCID: PMC11210259
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205880
THY1 is a prognostic-related biomarker via mediating immune infiltration in lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC)
Abstract
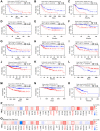
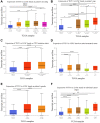
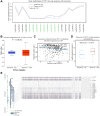
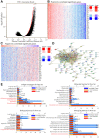
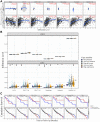
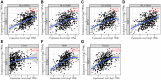
Thymus cell antigen 1 (THY1) has been proven to play pivotal roles in many diseases. However, we do not fully understand its functional mechanism, especially in lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). Here, we aimed to perform a comprehensive analysis to explore the expression and prognostic values of THY1 in LUSC using bioinformatic technology. Some online public databases (e.g., ONCOMINE, PrognoScan, TIMER, Kaplan-Meier plotter, STRING, LinkedOmics, and GEPIA) were used to explore the expression, prognostic significance, and potential molecular mechanism of THY1. The analysis indicated that THY1 was significantly up-regulated and closely correlated with poor prognosis in many malignant tumors, including LUSC. Further analysis revealed that over-expression of THY1 was significantly correlated with clinicopathological parameters (e.g., individual cancer stage, age, smoking habits, nodal metastasis status, and TP53 mutation status) in LUSC. The CpG islands methylation of THY1 was negatively correlated with THY1 mRNA expression in The Cancer Genome Atlas Program (TCGA). Further enrichment analysis of THY1 correlated genes revealed that they were mainly correlated with the formation of extracellular matrix (ECM), and got involved in the pathway of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT). Furthermore, differentially expressed THY1 was significantly correlated with immune cell infiltrations and poor prognosis in LUSC. In summary, bioinformatic analysis demonstrated that THY1 was significantly over-expressed and closely correlated with unfavorable prognosis in LUSC, which may apply as a promising diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker for LUSC in the future.
Keywords: LUSC; THY1; bioinformatics; biomarker; immune infiltration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Borghaei H, Chang AC, Cheney RT, Chirieac LR, D'Amico TA, Demmy TL, Govindan R, Grannis FW Jr, Grant SC, Horn L, Jahan TM, et al. , and National comprehensive cancer network. Non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2013. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2013; 11:645–53. 10.6004/jnccn.2013.0084 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lung HL, Cheung AK, Cheng Y, Kwong FM, Lo PH, Law EW, Chua D, Zabarovsky ER, Wang N, Tsao SW, Stanbridge EJ, Lung ML. Functional characterization of THY1 as a tumor suppressor gene with antiinvasive activity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2010; 127:304–12. 10.1002/ijc.25047 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

