The tumor-intrinsic role of the m6A reader YTHDF2 in regulating immune evasion
- PMID: 38820140
- PMCID: PMC12068375
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adl2171
The tumor-intrinsic role of the m6A reader YTHDF2 in regulating immune evasion
Abstract
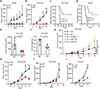
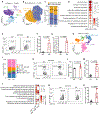
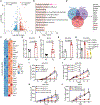
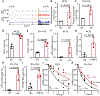
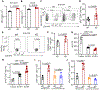
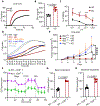
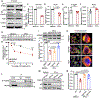
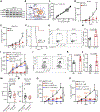
Tumors evade attacks from the immune system through various mechanisms. Here, we identify a component of tumor immune evasion mediated by YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2), a reader protein that usually destabilizes m6A-modified mRNA. Loss of tumoral YTHDF2 inhibits tumor growth and prolongs survival in immunocompetent tumor models. Mechanistically, tumoral YTHDF2 deficiency promotes the recruitment of macrophages via CX3CL1 and enhances mitochondrial respiration of CD8+ T cells by impairing tumor glycolysis metabolism. Tumoral YTHDF2 deficiency promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and antigen presentation in the presence of IFN-γ. In addition, IFN-γ induces autophagic degradation of tumoral YTHDF2, thereby sensitizing tumor cells to CD8+ T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Last, we identified a small molecule compound that preferentially induces YTHDF2 degradation, which shows a potent antitumor effect alone but a better effect when combined with anti-PD-L1 or anti-PD-1 antibodies. Collectively, YTHDF2 appears to be a tumor-intrinsic regulator that orchestrates immune evasion, representing a promising target for enhancing cancer immunotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Hanahan D, Hallmarks of cancer: New dimensions. Cancer Discov. 12, 31–46 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS106170/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N93022D00005/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N99020D00005/OF/ORFDO NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA266457/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA210087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA264512/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA163205/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA247550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA265095/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N93023D00005/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI129582/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA033572/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N95020D00005/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

