5-HT receptors exert differential effects on seizure-induced respiratory arrest in DBA/1 mice
- PMID: 38820310
- PMCID: PMC11142501
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304601
5-HT receptors exert differential effects on seizure-induced respiratory arrest in DBA/1 mice
Abstract
Both clinical and animal studies demonstrated that seizure-induced respiratory arrest (S-IRA) contributes importantly to sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP). It has been shown that enhancing serotonin (5-HT) function relieves S-IRA in animal models of SUDEP, including DBA/1 mice. Direct activation of 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptors suppresses S-IRA in DBA/1 mice, indicating that these receptors are involved in S-IRA. However, it remains unknown if other subtypes of 5-HT receptors are implicated in S-IRA in DBA/1 mice. In this study, we investigated the action of an agonist of the 5-HT1A (8-OH-DPAT), 5-HT2A (TCB-2), 5-HT2B (BW723C86), 5-HT2C (MK-212), 5-HT6 (WAY-208466) and 5-HT7 (LP-211) receptor on S-IRA in DBA/1 mice. An agonist of the 5-HT receptor or a vehicle was intraperitoneally administered 30 min prior to acoustic simulation, and the effect of each drug/vehicle on the incidence of S-IRA was videotaped for offline analysis. We found that the incidence of S-IRA was significantly reduced by TCB-2 at 10 mg/kg (30%, n = 10; p < 0.01, Fisher's exact test) but was not altered by other agonists compared with the corresponding vehicle controls in DBA/1 mice. Our data demonstrate that 5-HT2A receptors are implicated in S-IRA, and 5-HT1A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 receptors are not involved in S-IRA in DBA/1 mice.
Copyright: © 2024 Pan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

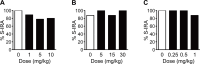
Similar articles
-
Serotonin 5-HT4 receptors play a critical role in the action of fenfluramine to block seizure-induced sudden death in a mouse model of SUDEP.Epilepsy Res. 2021 Nov;177:106777. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2021.106777. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Epilepsy Res. 2021. PMID: 34601387
-
Abnormalities of serotonergic neurotransmission in animal models of SUDEP.Epilepsy Behav. 2017 Jun;71(Pt B):174-180. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Epilepsy Behav. 2017. PMID: 26272185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optogenetic activation of 5-HT neurons in the dorsal raphe suppresses seizure-induced respiratory arrest and produces anticonvulsant effect in the DBA/1 mouse SUDEP model.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Feb;110:47-58. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 29141182 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic agents act on 5-HT3 receptors in the brain to block seizure-induced respiratory arrest in the DBA/1 mouse model of SUDEP.Epilepsy Behav. 2016 Nov;64(Pt A):166-170. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.09.034. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Epilepsy Behav. 2016. PMID: 27743549 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the neuroendocrine role of serotonin.Dan Med Bull. 2007 Nov;54(4):266-88. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 18208678 Review.
Cited by
-
Lethal Interactions of neuronal networks in epilepsy mediated by both synaptic and volume transmission indicate approaches to prevention.Prog Neurobiol. 2025 Jun;249:102770. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2025.102770. Epub 2025 Apr 19. Prog Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40258456 Review.
References
-
- Nakase K, Kollmar R, Lazar J, Arjomandi H, Sundaram K, Silverman J, et al.. Laryngospasm, central and obstructive apnea during seizures: Defining pathophysiology for sudden death in a rat model. Epilepsy research. 2016;128:126–39. Epub 20161027. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.08.004 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

