A comprehensive protocol for quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of the brain at 3 Tesla
- PMID: 38820354
- PMCID: PMC11142522
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297244
A comprehensive protocol for quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of the brain at 3 Tesla
Abstract
Quantitative MRI (qMRI) has been shown to be clinically useful for numerous applications in the brain and body. The development of rapid, accurate, and reproducible qMRI techniques offers access to new multiparametric data, which can provide a comprehensive view of tissue pathology. This work introduces a multiparametric qMRI protocol along with full postprocessing pipelines, optimized for brain imaging at 3 Tesla and using state-of-the-art qMRI tools. The total scan time is under 50 minutes and includes eight pulse-sequences, which produce range of quantitative maps including T1, T2, and T2* relaxation times, magnetic susceptibility, water and macromolecular tissue fractions, mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy, magnetization transfer ratio (MTR), and inhomogeneous MTR. Practical tips and limitations of using the protocol are also provided and discussed. Application of the protocol is presented on a cohort of 28 healthy volunteers and 12 brain regions-of-interest (ROIs). Quantitative values agreed with previously reported values. Statistical analysis revealed low variability of qMRI parameters across subjects, which, compared to intra-ROI variability, was x4.1 ± 0.9 times higher on average. Significant and positive linear relationship was found between right and left hemispheres' values for all parameters and ROIs with Pearson correlation coefficients of r>0.89 (P<0.001), and mean slope of 0.95 ± 0.04. Finally, scan-rescan stability demonstrated high reproducibility of the measured parameters across ROIs and volunteers, with close-to-zero mean difference and without correlation between the mean and difference values (across map types, mean P value was 0.48 ± 0.27). The entire quantitative data and postprocessing scripts described in the manuscript are publicly available under dedicated GitHub and Figshare repositories. The quantitative maps produced by the presented protocol can promote longitudinal and multi-center studies, and improve the biological interpretability of qMRI by integrating multiple metrics that can reveal information, which is not apparent when examined using only a single contrast mechanism.
Copyright: © 2024 Radunsky et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
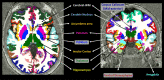
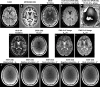
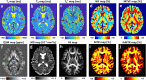


Similar articles
-
How stable is quantitative MRI? - Assessment of intra- and inter-scanner-model reproducibility using identical acquisition sequences and data analysis programs.Neuroimage. 2020 Feb 15;207:116364. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116364. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 31740340
-
Application of Anti-Motion Ultra-Fast Quantitative MRI in Neurological Disorder Imaging: Insights From Huntington's Disease.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 Jun;61(6):2455-2468. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29682. Epub 2025 Jan 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39887812
-
Multiparametric Quantitative MRI of Peripheral Nerves in the Leg: A Reliability Study.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Feb;59(2):563-574. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28778. Epub 2023 May 16. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37191075 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Multiparametric Quantitative Brain MRI: State-of-the-Art Relaxometric and Proton Density Mapping Techniques.Radiology. 2022 Oct;305(1):5-18. doi: 10.1148/radiol.211519. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Radiology. 2022. PMID: 36040334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Biomarkers of Muscle.Tomography. 2024 Sep 2;10(9):1411-1438. doi: 10.3390/tomography10090106. Tomography. 2024. PMID: 39330752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mara C, Nicholas GD, Paul ST. Quantitative MRI of the brain: Principles of physical measurement. 2nd ed. CRC Press, 2018.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

