Association between (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP and in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A secondary analysis
- PMID: 38820377
- PMCID: PMC11142544
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304518
Association between (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP and in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A secondary analysis
Abstract
Background: The arterial pressure of oxygen (PaO2)/inspiratory fraction of oxygen (FiO2) is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia. ΔPaO2/FiO2 [the difference between PaO2/FiO2 after 24 h of invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) and PaO2/FiO2 before IMV] is associated with in-hospital mortality. However, the value of PaO2 can be influenced by the end-expiratory pressure (PEEP). To the best of our knowledge, the relationship between the ratio of (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP and in-hospital mortality remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate their association.
Methods: The study was conducted in southern Peru from April 2020 to April 2021. A total of 200 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia requiring IMV were included in the present study. We analyzed the association between (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP and in-hospital mortality by Cox proportional hazards regression models.
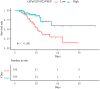
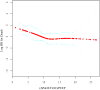
Results: The median (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP was 11.78 mmHg/cmH2O [interquartile range (IQR) 8.79-16.08 mmHg/cmH2O], with a range of 1 to 44.36 mmHg/cmH2O. Patients were divided equally into two groups [low group (< 11.80 mmHg/cmH2O), and high group (≥ 11.80 mmHg/cmH2O)] according to the (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP ratio. In-hospital mortality was lower in the high (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP group than in the low (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP group [18 (13%) vs. 38 (38%)]; hazard ratio (HR), 0.33 [95% confidence intervals (CI), 0.17-0.61, P < 0.001], adjusted HR, 0.32 (95% CI, 0.11-0.94, P = 0.038). The finding that the high (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP group exhibited a lower risk of in-hospital mortality compared to the low (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP group was consistent with the results from the sensitivity analysis. After adjusting for confounding variables, we found that each unit increase in (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP was associated with a 12% reduction in the risk of in-hospital mortality (HR, 0.88, 95%CI, 0.80-0.97, P = 0.013).
Conclusions: The (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP ratio was associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. (ΔPaO2/FiO2)/PEEP might be a marker of disease severity in COVID-19 patients.
Copyright: © 2024 Chen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between PaO2/(FiO2*PEEP) ratio and in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients: A reanalysis of published data from Peru using PaO2/(FiO2*PEEP) ratio in place of PaO2/FaO2 ratio.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 4;103(40):e39931. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039931. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465757 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of PaO2/FiO2 after 24 h of invasive mechanical ventilation and ΔPaO2/FiO2 at 24 h as predictors of survival in patients diagnosed with ARDS due to COVID-19.PeerJ. 2022 Dec 13;10:e14290. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14290. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36530414 Free PMC article.
-
Response to Ventilator Adjustments for Predicting Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Mortality. Driving Pressure versus Oxygenation.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021 May;18(5):857-864. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202007-862OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021. PMID: 33112644 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariable fractional polynomial interaction to investigate continuous effect modifiers in a meta-analysis on higher versus lower PEEP for patients with ARDS.BMJ Open. 2016 Sep 8;6(9):e011148. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011148. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27609843 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a positive end-expiratory pressure strategy on oxygenation, respiratory compliance, and hemodynamics during laparoscopic surgery in non-obese patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Nov 11;23(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02337-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37950169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scendoni R, Gattari D, Cingolani M. COVID-19 Pulmonary Pathology, Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury (VILI), or Sepsis-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)? Healthcare Considerations Arising From an Autopsy Case and Miny-Review. Clin Pathol. 2022; 15:2632010X221083223. doi: 10.1177/2632010X221083223 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Petrilli CM, Jones SA, Yang J, Rajagopalan H, O’Donnell L, Chernyak Y, et al.. Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020; 369:m1966. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1966 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous