Corporate social responsibility: A key driver of sustainable development in China's post-COVID economy
- PMID: 38820478
- PMCID: PMC11142668
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300209
Corporate social responsibility: A key driver of sustainable development in China's post-COVID economy
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Corporate social responsibility: A key driver of sustainable development in China's post-COVID economy.PLoS One. 2025 May 7;20(5):e0323216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323216. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40333677 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
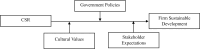
The first goal of this research was to measure the impact of corporate social responsibility (CSR) on the sustainable development of an organization. However, the second objective examines the moderating influence of government policies, cultural norms, and stakeholder expectations on the relationship between CSR and an organization's sustainable development. This research primarily focused on the enterprises operating in the energy industry in Beijing. A sample of 498 individuals holding management positions within these enterprises was collected. The study's results established that CSR significantly influences the sustainable development of firms. Moreover, the results revealed that governmental regulations, cultural norms, and stakeholder expectations play a significant and positive role in moderating the impact of corporate social responsibility on the sustainable development of companies. The results of this study make a valuable contribution to the existing body of literature on CSR and its impact on the sustainable performance of enterprises in China.
Copyright: © 2024 Salman et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Saba Ahmed D., et al.., Infodemics: A Post Pandemic Perspective Of Covid-19. Webology (ISSN: 1735-188X), 2021. 18(6).
-
- Parsa S., et al.., Corporate social responsibility reporting in China: Political, social and corporate influences. Accounting and Business Research, 2021. 51(1): p. 36–64.
-
- Rim H., Kim J., and Dong C., A cross‐national comparison of transparency signaling in corporate social responsibility reporting: The United States, South Korea, and China cases. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 2019. 26(6): p. 1517–1529.
-
- Khan A.J., et al.., Green HRM and employee efficiency: The mediating role of employee motivation in emerging small businesses. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022: p. 2233.
-
- Kang J., Diao Z., and Zanini M.T., Business-to-business marketing responses to COVID-19 crisis: a business process perspective. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 2021. 39(3): p. 454–468.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

