Clinical value of nano-carbon lymphatic tracer for regional lymph node dissections of rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
- PMID: 38820538
- PMCID: PMC11302801
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.14406
Clinical value of nano-carbon lymphatic tracer for regional lymph node dissections of rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
Abstract
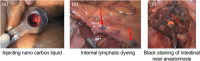
Objectives: Regional lymph node (LN) volume decreases after neoadjuvant therapy, requiring a tracer for more accurate detection. Nano-carbon tracer is a third-generation tracer with several advantages, but its use for LN detection after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for middle and low rectal cancer remains unclear. Therefore, this study investigated the effects and safety of anoscope-guided subrectal injections of nano-carbon suspension in this patient population.
Methods: This study retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 45 patients with middle and low rectal cancer admitted to our institution from March 2019 to March 2022. All patients received preoperative neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy and were divided into nano-carbon injection (n = 23; anoscope-guided injections of nano-carbon suspension in the rectal submucosa 2 cm above the dentate line 24 h preoperatively) and control (n = 22; directly underwent surgery) groups. The LN detection and complication rates were compared between the groups.
Results: The total and mean numbers of LNs and small LNs and the number of patients with > 12 LNs were significantly higher in the nano-carbon injection group than in the control group. The total number of positive LNs and LN metastasis did not differ between the groups, nor did the anastomotic leakage, bleeding, stenosis, and abscess occurrence rates.
Conclusions: Anoscope-guided nano-carbon lymphatic tracing increased the LN detection rate, caused less trauma, and resulted in fewer postoperative complications than the direct surgical procedure. Thus, it is an effective, safe, and practical method that may improve dissections and the postoperative pathological staging accuracy.
Keywords: lymph node; nano‐carbon; pathological staging; rectal cancer; tracer.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lymph node ratio is an independent prognostic factor in node positive rectal cancer patients treated with preoperative chemoradiotherapy followed by curative resection.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(13):5365-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.13.5365. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25041003
-
Prognostic value of metastatic lymph node regression grade after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer.Surgery. 2019 Dec;166(6):1061-1067. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2019.06.009. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Surgery. 2019. PMID: 31345564
-
Nodal staging with MRI after neoadjuvant chemo-radiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: a fast and reliable method.Eur Radiol. 2024 May;34(5):3205-3214. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10265-3. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37930408
-
[Analysis on efficacy and safety of total neoadjuvant therapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer with high risk factors].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Apr 25;22(4):349-356. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0274.2019.04.007. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31054549 Chinese.
-
The effects of preoperative chemoradiotherapy on lymph node sampling in rectal cancer.Dis Colon Rectum. 2012 Sep;55(9):1002-7. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0b013e3182536d70. Dis Colon Rectum. 2012. PMID: 22874609 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of nano-carbon suspension lymph node tracing on rectal cancer surgery post-neoadjuvant therapy.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2025 Aug 19;40(1):182. doi: 10.1007/s00384-025-04982-y. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2025. PMID: 40830708 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of endoscopic neodymium-iron-boron magnet ring tracer technique in laparoscopy for colorectal lesions.Endoscopy. 2024 Dec;56(S 01):E1135-E1136. doi: 10.1055/a-2499-7462. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Endoscopy. 2024. PMID: 39701560 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Martín MJ, Gentili C, Lassalle V. In vitro biological tests as the first tools to validate magnetic nanotheranostics for colorectal cancer models. ChemMedChem. 2020;15:1003‐1017. - PubMed
-
- Ünal S. Akta çY, Benito JM, Bilensoy E. Cyclodextrin nanoparticle bound oral camptothecin for colorectal cancer: formulation development and optimization. Int J Pharm. 2020;584:119468. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Deng X, Wang L, Liu J, Xu K. Clinical application of carbon nanoparticles in lymphatic mapping during colorectal cancer surgeries: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52:1445‐1454. - PubMed
-
- Jin KT, Yao JY, Ying XJ, Lin Y, Chen YF. Nanomedicine and early cancer diagnosis: molecular imaging using fluorescence nanoparticles. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20:2737‐2761. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources