Ivonescimab Plus Chemotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer With EGFR Variant: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38820549
- PMCID: PMC11337070
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2024.10613
Ivonescimab Plus Chemotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer With EGFR Variant: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: For patients with non-small cell lung cancer whose disease progressed while receiving EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) therapy, particularly third-generation TKIs, optimal treatment options remain limited.
Objective: To compare the efficacy of ivonescimab plus chemotherapy with chemotherapy alone for patients with relapsed advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) variant.
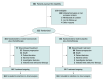
Design, setting, and participants: Double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, phase 3 trial at 55 sites in China enrolled participants from January 2022 to November 2022; a total of 322 eligible patients were enrolled.
Interventions: Participants received ivonescimab (n = 161) or placebo (n = 161) plus pemetrexed and carboplatin once every 3 weeks for 4 cycles, followed by maintenance therapy of ivonescimab plus pemetrexed or placebo plus pemetrexed.
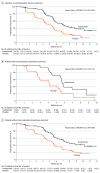
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was progression-free survival in the intention-to-treat population assessed by an independent radiographic review committee (IRRC) per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1. The results of the first planned interim analysis are reported.
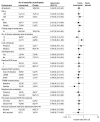
Results: Among 322 enrolled patients in the ivonescimab and placebo groups, the median age was 59.6 vs 59.4 years and 52.2% vs 50.9% of patients were female. As of March 10, 2023, median follow-up time was 7.89 months. Median progression-free survival was 7.1 (95% CI, 5.9-8.7) months in the ivonescimab group vs 4.8 (95% CI, 4.2-5.6) months for placebo (difference, 2.3 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.46 [95% CI, 0.34-0.62]; P < .001). The prespecified subgroup analysis showed progression-free survival benefit favoring patients receiving ivonescimab over placebo across almost all subgroups, including patients whose disease progressed while receiving third-generation EGFR-TKI therapy (HR, 0.48 [95% CI 0.35-0.66]) and those with brain metastases (HR, 0.40 [95% CI, 0.22-0.73]). The objective response rate was 50.6% (95% CI, 42.6%-58.6%) with ivonescimab and 35.4% (95% CI, 28.0%-43.3%) with placebo (difference, 15.6% [95% CI, 5.3%-26.0%]; P = .006). The median overall survival data were not mature; at data cutoff, 69 patients (21.4%) had died. Grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 99 patients (61.5%) in the ivonescimab group vs 79 patients (49.1%) in the placebo group, the most common of which were chemotherapy-related. Grade 3 or higher immune-related adverse events occurred in 10 patients (6.2%) in the ivonescimab group vs 4 (2.5%) in the placebo group. Grade 3 or higher vascular endothelial growth factor-related adverse events occurred in 5 patients (3.1%) in the ivonescimab group vs 4 (2.5%) in the placebo group.
Conclusions: Ivonescimab plus chemotherapy significantly improved progression-free survival with tolerable safety profile in TKI-treated non-small cell lung cancer.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05184712.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Finding the right HARMONi-A.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 31;13(12):3835-3837. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-864. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39830738 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mok T, Nakagawa K, Park K, et al. Nivolumab plus chemotherapy in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after disease progression on epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: final results of CheckMate 722. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(11):1252-1264. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.01017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

