Mast cells control lung type 2 inflammation via prostaglandin E2-driven soluble ST2
- PMID: 38821053
- PMCID: PMC11168874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.05.003
Mast cells control lung type 2 inflammation via prostaglandin E2-driven soluble ST2
Abstract
Severe asthma and sinus disease are consequences of type 2 inflammation (T2I), mediated by interleukin (IL)-33 signaling through its membrane-bound receptor, ST2. Soluble (s)ST2 reduces available IL-33 and limits T2I, but little is known about its regulation. We demonstrate that prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) drives production of sST2 to limit features of lung T2I. PGE2-deficient mice display diminished sST2. In humans with severe respiratory T2I, urinary PGE2 metabolites correlate with serum sST2. In mice, PGE2 enhanced sST2 secretion by mast cells (MCs). Mice lacking MCs, ST2 expression by MCs, or E prostanoid (EP)2 receptors by MCs showed reduced sST2 lung concentrations and strong T2I. Recombinant sST2 reduced T2I in mice lacking PGE2 or ST2 expression by MCs back to control levels. PGE2 deficiency also reversed the hyperinflammatory phenotype in mice lacking ST2 expression by MCs. PGE2 thus suppresses T2I through MC-derived sST2, explaining the severe T2I observed in low PGE2 states.
Keywords: IL33; ST2; aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease; asthma; mast cells; nasal polyps; prostaglandin E(2); type 2 inflammation.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
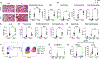


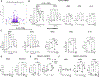
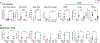
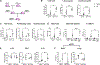

Comment in
-
Mast cells: The Janus of type 2 inflammation.Immunity. 2024 Jun 11;57(6):1182-1184. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.05.011. Immunity. 2024. PMID: 38865961
References
-
- Wu W, Bleecker E, Moore W, Busse WW, Castro M, Chung KF, Calhoun WJ, Erzurum S, Gaston B, Israel E, et al. (2014). Unsupervised phenotyping of Severe Asthma Research Program participants using expanded lung data. J Allergy Clin Immunol 133, 1280–1288. 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.11.042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stevens WW, Peters AT, Hirsch AG, Nordberg CM, Schwartz BS, Mercer DG, Mahdavinia M, Grammer LC, Hulse KE, Kern RC, et al. (2017). Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps, Asthma, and Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 5, 1061–1070 e1063. 10.1016/j.jaip.2016.12.027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carriere V, Roussel L, Ortega N, Lacorre DA, Americh L, Aguilar L, Bouche G, and Girard JP (2007). IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 104, 282–287. 04 [pii]; 10.1073/pnas.0606854104 [doi]. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scott IC, Majithiya JB, Sanden C, Thornton P, Sanders PN, Moore T, Guscott M, Corkill DJ, Erjefält JS, and Cohen ES (2018). Interleukin-33 is activated by allergen- and necrosis-associated proteolytic activities to regulate its alarmin activity during epithelial damage. Scientific Reports 8, 3363. 10.1038/s41598-018-21589-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

