Nivolumab plus relatlimab in patients with previously treated microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: the phase II CheckMate 142 study
- PMID: 38821718
- PMCID: PMC11149130
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008689
Nivolumab plus relatlimab in patients with previously treated microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: the phase II CheckMate 142 study
Abstract
Background: Programmed death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors, including nivolumab, have demonstrated long-term survival benefit in previously treated patients with microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient (MSI-H/dMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC). PD-1 and lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG-3) are distinct immune checkpoints that are often co-expressed on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and contribute to tumor-mediated T-cell dysfunction. Relatlimab is a LAG-3 inhibitor that has demonstrated efficacy in combination with nivolumab in patients with melanoma. Here, we present the results from patients with MSI-H/dMMR metastatic CRC treated with nivolumab plus relatlimab in the CheckMate 142 study.
Methods: In this open-label, phase II study, previously treated patients with MSI-H/dMMR metastatic CRC received nivolumab 240 mg plus relatlimab 160 mg intravenously every 2 weeks. The primary end point was investigator-assessed objective response rate (ORR).
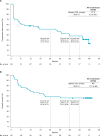
Results: A total of 50 previously treated patients received nivolumab plus relatlimab. With median follow-up of 47.4 (range 43.9-49.2) months, investigator-assessed ORR was 50% (95% CI 36% to 65%) and disease control rate was 70% (95% CI 55% to 82%). The median time to response per investigator was 2.8 (range 1.3-33.1) months, and median duration of response was 42.7 (range 2.8-47.0+) months. The median progression-free survival per investigator was 27.5 (95% CI 5.3 to 43.7) months with a progression-free survival rate at 3 years of 38%, and median overall survival was not reached (95% CI 17.2 months to not estimable), with a 56% overall survival rate at 3 years. The most common any-grade treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were diarrhea (24%), asthenia (16%), and hypothyroidism (12%). Grade 3 or 4 TRAEs were reported in 14% of patients, and TRAEs of any grade leading to discontinuation were observed in 8% of patients. No treatment-related deaths were reported.
Conclusions: Nivolumab plus relatlimab provided durable clinical benefit and was well tolerated in previously treated patients with MSI-H/dMMR metastatic CRC.
Trial registration number: NCT02060188.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitor.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MJO reports consulting fees from Phanes Therapeutics, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Merck, GSK, Nouscom, Tempus, Roche, Bayer, Ellipses Pharma, Simcere, and Gritstone, and research grants from Roche, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, and Nouscom. FG reports consulting or advisory role for Merck Serono and Amgen; and speakers’ bureau for Servier, Eli Lilly, IQVIA, and Bristol Myers Squibb. MLLM reports payments/honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb. GL reports consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, honoraria from Merck Servier, and travel support from Roche. PG-A reports payment/honoraria for speakers’ bureaus from Amgen, Roche, Merck Serono, Sanofi-Aventis, Pierre Fabre, Servier, MSD, Organon, and Ipsen; travel expenses from Amgen, Roche, Merck Serono, Sanofi-Aventis, Pierre Fabre, Servier, and MSD, and advisory activities for Amgen, Roche, Merck Serono, Sanofi-Aventis, Pierre Fabre, and Servier. EVC reports participation in advisory boards for Array BioPharma, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biocartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Halozyme, GSK, Incyte, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck KGaA, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Servier, Sirtex Medical, and Taiho Pharmaceutical; and research funding from Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Ipsen, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck KGaA, Novartis, Roche, and Servier, paid to his institution. BE-R reports grants or contracts from AstraZeneca, Exelixis, EUSA Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Novartis, and Xencor; and consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dicephera, Ipsen, Neogenomics, Roche, and Seagen. SMMcC reports being an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb, owning stocks from Diversified Portfolio, and holding patents from RJS Biologics. BH reports owning stocks and being an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb. ML reports being an employee of, owning stock in, and being an inventor of patents filed/owned by Bristol Myers Squibb. SL reports research funding from Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Hutchinson, Incyte, Merck Serono, Mirati, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, and Servier; consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Incyte, Lilly, Merck Serono, MSD, and Servier, and payment/honoraria for lectures/presentations from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, GSK, Lilly, Merck Serono, MSD, Pierre-Fabre, Roche, and Servier. MA, MW, AGH, and ACG report no conflicts of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Tougeron D, Cohen R, Sueur B, et al. . A large retrospective multicenter study evaluating prognosis and chemosensitivity of metastatic colorectal cancer with microsatellite instability. Ann Oncol 2017;28:v180. 10.1093/annonc/mdx393.059 - DOI
-
- André T, Lonardi S, Wong KYM, et al. . Nivolumab plus low-dose ipilimumab in previously treated patients with microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: 4-year follow-up from CheckMate 142. Ann Oncol 2022;33:1052–60:S0923-7534(22)01737-9. 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.06.008 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
