Leveraging the fundamentals of heat transfer and fluid mechanics in microscale geometries for automated next-generation sequencing library preparation
- PMID: 38822053
- PMCID: PMC11637099
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63014-x
Leveraging the fundamentals of heat transfer and fluid mechanics in microscale geometries for automated next-generation sequencing library preparation
Abstract
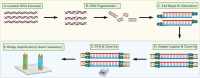
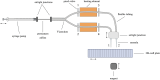
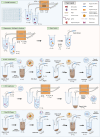
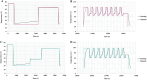
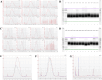
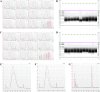
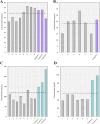
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is emerging as a powerful tool for molecular diagnostics but remains limited by cumbersome and inefficient sample preparation. We present an innovative automated NGS library preparation system with a simplified mechanical design that exploits both macro- and microfluidic properties for optimizing heat transfer, reaction kinetics, mass transfer, fluid mechanics, adsorption-desorption rates, and molecular thermodynamics. Our approach introduces a unique two-cannula cylindrical capillary system connected to a programmable syringe pump and a Peltier heating element able to execute all steps with high efficiency. Automatic reagent movement, mixing, and magnetic bead-based washing with capillary-based thermal cycling (capillary-PCR) are completely integrated into a single platform. The manual 3-h library preparation process is reduced to less than 15 min of hands-on time via optimally pre-plated reagent plates, followed by less than 6 h of instrument run time during which no user interaction is required. We applied this method to two library preparation assays with different DNA fragmentation requirements (mechanical vs. enzymatic fragmentation), sufficiently limiting consumable use to one cartridge and one 384 well-plate per run. Our platform successfully prepared eight libraries in parallel, generating sequencing data for both human and Escherichia coli DNA libraries with negligible coverage bias compared to positive controls. All sequencing data from our libraries attained Phred (Q) scores > 30, mapping to reference genomes at 99% confidence. The method achieved final library concentrations and size distributions comparable with the conventional manual approach, demonstrating compatibility with downstream sequencing and subsequent data analysis. Our engineering design offers repeatability and consistency in the quality of sequence-able libraries, asserting the importance of mechanical design considerations that employ and optimize fundamental fluid mechanics and heat transfer properties. Furthermore in this work, we provide unique insights into the mechanisms of sample loss within NGS library preparation assays compared with automated adaptations and pinpoint areas in which the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer can improve future mechanical design iterations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. AT is a paid scientific advisor/consultant for Revvity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peripheral blood to next-generation sequencing ready DNA library: a novel engineering design for automation.BMC Genomics. 2024 Oct 22;25(1):987. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10892-0. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39438788 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated magneto-electrophoresis microfluidic chip purification on library preparation device for preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy detection.RSC Adv. 2021 Apr 16;11(24):14459-14474. doi: 10.1039/d1ra01732b. eCollection 2021 Apr 15. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35423999 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent amplification for next generation sequencing (FA-NGS) library preparation.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jan 28;21(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6481-8. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 31992180 Free PMC article.
-
Library preparation methods for next-generation sequencing: tone down the bias.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Mar 10;322(1):12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24440557 Review.
-
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) in the microbiological world: How to make the most of your money.J Microbiol Methods. 2017 Jul;138:60-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2016.02.016. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Microbiol Methods. 2017. PMID: 26995332 Review.
References
-
- Schweiger, M. R., Kerick, M., Timmermann, B. & Isau, M. The power of NGS technologies to delineate the genome organization in cancer: From mutations to structural variations and epigenetic alterations. Cancer Metastasis Rev.30(2), 199–210 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Servetto, A. et al. A review of the use of next generation sequencing methodologies to identify biomarkers of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER+/HER2- breast cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol.157, 103191 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

