Mediator kinase inhibition impedes transcriptional plasticity and prevents resistance to ERK/MAPK-targeted therapy in KRAS-mutant cancers
- PMID: 38822082
- PMCID: PMC11143207
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-024-00615-9
Mediator kinase inhibition impedes transcriptional plasticity and prevents resistance to ERK/MAPK-targeted therapy in KRAS-mutant cancers
Abstract
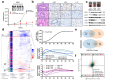
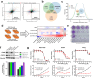
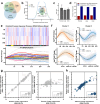
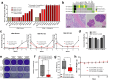
Acquired resistance remains a major challenge for therapies targeting oncogene activated pathways. KRAS is the most frequently mutated oncogene in human cancers, yet strategies targeting its downstream signaling kinases have failed to produce durable treatment responses. Here, we developed multiple models of acquired resistance to dual-mechanism ERK/MAPK inhibitors across KRAS-mutant pancreatic, colorectal, and lung cancers, and then probed the long-term events enabling survival against this class of drugs. These studies revealed that resistance emerges secondary to large-scale transcriptional adaptations that are diverse and cell line-specific. Transcriptional reprogramming extends beyond the well-established early response, and instead represents a dynamic, evolved process that is refined to attain a stably resistant phenotype. Mechanistic and translational studies reveal that resistance to dual-mechanism ERK/MAPK inhibition is broadly susceptible to manipulation of the epigenetic machinery, and that Mediator kinase, in particular, can be co-targeted at a bottleneck point to prevent diverse, cell line-specific resistance programs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.C.W. is a founder, consultant, and equity holder at Tavros Therapeutics and Celldom and has performed consulting work for Guidepoint Global, Bantam Pharmaceuticals, and Apple Tree Partners. C.J.D. is an advisory board member for Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, Mirati Therapeutics, Reactive Biosciences, Revolution Medicines and SHY Therapeutics, has received research funding support from Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, Mirati Therapeutics, Reactive Biosciences, Revolution Medicines and SpringWorks Therapeutics, and has consulted for Day One Biotherapeutics, Eli Lilly, Jazz Therapeutics, Ribometrix, Sanofi, and Turning Point Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests. JJS received travel support for fellow education from Intuitive Surgical (August 2015). He also served as a clinical advisor for Guardant Health (March 2019) and as a clinical advisor for Foundation Medicine (April 2022). He served as a consultant and speaker for Johnson and Johnson (May 2022). And he serves as a clinical advisor and consultant for GlaxoSmithKline (2023-24).
Figures

Update of
-
Mediator Kinase Inhibition Impedes Transcriptional Plasticity and Prevents Resistance to ERK/MAPK-Targeted Therapy in KRAS-Mutant Cancers.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 2:rs.3.rs-3511242. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3511242/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 May 31;8(1):124. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00615-9. PMID: 37961649 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Mediator Kinase Inhibition Impedes Transcriptional Plasticity and Prevents Resistance to ERK/MAPK-Targeted Therapy in KRAS-Mutant Cancers.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 2:rs.3.rs-3511242. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3511242/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 May 31;8(1):124. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00615-9. PMID: 37961649 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
SOS1 and KSR1 modulate MEK inhibitor responsiveness to target resistant cell populations based on PI3K and KRAS mutation status.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Nov 21;120(47):e2313137120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313137120. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37972068 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of SUMOylation and MEK conquers MYC-expressing KRAS-mutant cancers by accumulating DNA damage.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Jul 11;31(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01060-3. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38992694 Free PMC article.
-
Back to the Bench? MEK and ERK Inhibitors for the Treatment of KRAS Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma.Curr Med Chem. 2018 Feb 13;25(5):558-574. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170530093100. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28554329 Review.
-
Dual Inhibition of MEK and PI3K Pathway in KRAS and BRAF Mutated Colorectal Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 23;16(9):22976-88. doi: 10.3390/ijms160922976. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26404261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mediator Kinase Inhibitor Selectivity and Activity in Colorectal Cancer.ACS Chem Biol. 2025 Jul 18;20(7):1792-1804. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5c00338. Epub 2025 Jul 2. ACS Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40601435 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative regulation of coupled oncoprotein synthesis and stability in triple-negative breast cancer by EGFR and CDK12/13.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Sep 19;120(38):e2221448120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221448120. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37695916 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting senescent stemlike subpopulations in Philadelphia chromosome-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Blood. 2025 Mar 13;145(11):1195-1210. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024026482. Blood. 2025. PMID: 39774844
References
Grants and funding
- F32 CA180569/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA175747/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- U01CA199235/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA175747/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA199235/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA207083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35CA232113/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R37 CA248289/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 CA276632/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32CA180569/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- P01 CA203657/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA232113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N/A (Start-Up Funds)/Duke University (Duke)
- W81XWH2110362/U.S. Department of Defense (United States Department of Defense)
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA268527/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- PF 18-061/American Cancer Society (American Cancer Society, Inc.)
- 5F32CA268527/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01CA207083/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01CA263593/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA263593/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM139550/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA203657/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

