Chemically engineered essential oils prepared through thiocyanation under solvent-free conditions: chemical and bioactivity alteration
- PMID: 38822174
- PMCID: PMC11143095
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-024-00456-w
Chemically engineered essential oils prepared through thiocyanation under solvent-free conditions: chemical and bioactivity alteration
Abstract
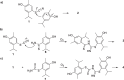
The generation of chemically engineered essential oils (CEEOs) prepared from bi-heteroatomic reactions using ammonium thiocyanate as a source of bioactive compounds is described. The impact of the reaction on the chemical composition of the mixtures was qualitatively demonstrated through GC-MS, utilizing univariate and multivariate analysis. The reaction transformed most of the components in the natural mixtures, thereby expanding the chemical diversity of the mixtures. Changes in inhibition properties between natural and CEEOs were demonstrated through acetylcholinesterase TLC autography, resulting in a threefold increase in the number of positive events due to the modification process. The chemically engineered Origanum vulgare L. essential oil was subjected to bioguided fractionation, leading to the discovery of four new active compounds with similar or higher potency than eserine against the enzyme. The results suggest that the directed chemical transformation of essential oils can be a valuable strategy for discovering new acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors; Ammonium thiocyanate; Bioactive compounds; Chemically modified essential oils; Iodine catalysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chemically engineered extracts: source of bioactive compounds.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Apr 19;44(4):241-50. doi: 10.1021/ar100106n. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21355557 Review.
-
A New Fluorinated Tyrosinase Inhibitor from a Chemically Engineered Essential Oil.ACS Comb Sci. 2016 Jun 13;18(6):283-6. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.6b00004. Epub 2016 May 13. ACS Comb Sci. 2016. PMID: 27144399
-
Chemical diversity in leaf and stem essential oils of Origanum vulgare L. and their effects on microbicidal activities.AMB Express. 2019 Oct 31;9(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s13568-019-0893-3. AMB Express. 2019. PMID: 31673872 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical composition, aroma evaluation, and inhibitory activity towards acetylcholinesterase of essential oils from Gynura bicolor DC.J Nat Med. 2016 Apr;70(2):282-9. doi: 10.1007/s11418-015-0961-1. Epub 2016 Jan 12. J Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 26758617
-
A Recent Insight Regarding the Phytochemistry and Bioactivity of Origanum vulgare L. Essential Oil.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 17;21(24):9653. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249653. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33348921 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New semisynthetic α-glucosidase inhibitor from a doubly-chemically engineered extract.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2025 Jan 5;15(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s13659-024-00488-2. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2025. PMID: 39755857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raut JS, Karuppayil SM. A status review on the medicinal properties of essential oils. Ind Crops Prod. 2014;62:250–264. doi: 10.1016/J.INDCROP.2014.05.055. - DOI
-
- Sell CS. The Chemistry of Fragrance. In Perfumer to Consumer. 2nd ed. The Royal Society of Chemistry; Cambridge, UK. 2006, p. 329.
Grants and funding
- 80020180300114UR/Universidad Nacional de Rosario
- 80020180100128UR/Universidad Nacional de Rosario
- 11220200102423/Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas
- PICT2015-3574/Fondo para la Investigación Científica y Tecnológica
- PICT2018-01554/Fondo para la Investigación Científica y Tecnológica
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

