Validation of the Korean version of the Summated Xerostomia Inventory among older adults residing in nursing homes
- PMID: 38822313
- PMCID: PMC11143705
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-18875-2
Validation of the Korean version of the Summated Xerostomia Inventory among older adults residing in nursing homes
Abstract
Background: Xerostomia is commonly experienced by older individuals. We sought to develop and evaluate the reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Summated Xerostomia Inventory (K-SXI) among older adults residing in long-term care facilities (LTCFs) in Korea.
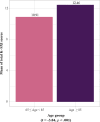
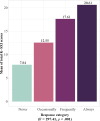
Methods: In this secondary data analysis study using cross-sectional data, a cross-cultural adaptation process was conducted for the Korean version before data collection. Data collection was conducted from July 2021 to January 2022, targeting 544 older adults in 16 LTCFs. Data analysis included intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) for test-retest reliability, and Cronbach's α for internal consistency reliability. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were used to verify construct and convergent validity. Test-retest analysis was performed 6 weeks after baseline. Convergent and concurrent validities were assessed with age group and the xerostomia standard single question, respectively.
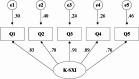
Results: A total of 544 older adults participated in this study. The mean of total K-SXI score was 11.70 (standard deviation, 4.96) points. The ICC value was calculated to be 0.90, and Cronbach's α of K-SXI was 0.92. Exploratory factor analysis revealed a single factor, explaining 74.8% of the total variance, however, some goodness-of-fit indices of the single factor model were found to be unsuitable in confirmatory factor analysis. The convergent and concurrent validity were supported.
Conclusion: The present study provides evidence supporting the validity and reliability of the K-SXI for measuring xerostomia in institutionalized older adults in Korea.
Keywords: Nursing home; Older adults; Reliability; Validity; Xerostomia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The validity and reliability of the Indonesian version of the Summated Xerostomia Inventory.Gerodontology. 2021 Mar;38(1):82-86. doi: 10.1111/ger.12494. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Gerodontology. 2021. PMID: 32935371 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Chinese version of the Summated Xerostomia Inventory (SXI).Qual Life Res. 2013 Dec;22(10):2843-7. doi: 10.1007/s11136-013-0420-y. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Qual Life Res. 2013. PMID: 23619629
-
Cross-cultural adaptation of the Thai Xerostomia Inventory and Summated Xerostomia Inventory.Oral Dis. 2024 Oct;30(7):4331-4340. doi: 10.1111/odi.14891. Epub 2024 Feb 11. Oral Dis. 2024. PMID: 38342965
-
Validity and reliability of the Hindi version of the Summated Xerostomia Inventory-5 among head and neck cancer irradiated patients in Delhi, India.J Cancer Res Ther. 2022 Dec;18(Supplement):S165-S169. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_1730_20. J Cancer Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36510959
-
Validating the Xerostomia Inventory in a radiation-induced xerostomia population in German language.Oral Dis. 2019 Oct;25(7):1744-1750. doi: 10.1111/odi.13154. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Oral Dis. 2019. PMID: 31295368
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- NRF2020R1A2C1100624/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government
- NRF2020R1A2C1100624/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government
- NRF2020R1A2C1100624/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government
- NRF2020R1A2C1100624/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government
- NRF2020R1A2C1100624/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical