N6-methyladenosine-modified SENP1, identified by IGF2BP3, is a novel molecular marker in acute myeloid leukemia and aggravates progression by activating AKT signal via de-SUMOylating HDAC2
- PMID: 38822351
- PMCID: PMC11141000
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-02013-y
N6-methyladenosine-modified SENP1, identified by IGF2BP3, is a novel molecular marker in acute myeloid leukemia and aggravates progression by activating AKT signal via de-SUMOylating HDAC2
Abstract
Background: Elevated evidence suggests that the SENPs family plays an important role in tumor progression. However, the role of SENPs in AML remains unclear.
Methods: We evaluated the expression pattern of SENP1 based on RNA sequencing data obtained from OHSU, TCGA, TARGET, and MILE datasets. Clinical samples were used to verify the expression of SENP1 in the AML cells. Lentiviral vectors shRNA and sgRNA were used to intervene in SENP1 expression in AML cells, and the effects of SENP1 on AML proliferation and anti-apoptosis were detected using in vitro and in vivo models. Chip-qPCR, MERIP-qPCR, CO-IP, RNA pulldown, and dual-luciferase reporter gene assays were used to explore the regulatory mechanisms of SNEP1 in AML.
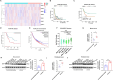
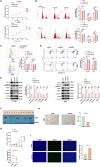
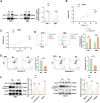
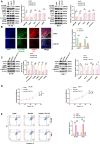
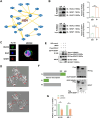
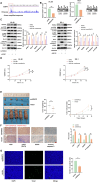
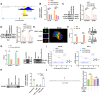
Results: SENP1 was significantly upregulated in high-risk AML patients and closely related to poor prognosis. The AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is a key downstream pathway that mediates SENP1's regulation of AML proliferation and anti-apoptosis. Mechanistically, the CO-IP assay revealed binding between SENP1 and HDAC2. SUMO and Chip-qPCR assays suggested that SENP1 can desumoylate HDAC2, which enhances EGFR transcription and activates the AKT pathway. In addition, we found that IGF2BP3 expression was upregulated in high-risk AML patients and was positively correlated with SENP1 expression. MERIP-qPCR and RIP-qPCR showed that IGF2BP3 binds SENP1 3-UTR in an m6A manner, enhances SENP1 expression, and promotes AKT pathway conduction.
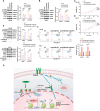
Conclusions: Our findings reveal a distinct mechanism of SENP1-mediated HDAC2-AKT activation and establish the critical role of the IGF2BP3/SENP1signaling axis in AML development.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; SENP1; SUMO; m6A.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SUMO-specific protease 1 exacerbates acute myeloid leukemia by enhancing beclin 1-dependent autophagy through polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 deSUMOylation.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Nov 27;116(6):1454-1468. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae143. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38934654
-
Licochalcone A decreases cancer cell proliferation and enhances ferroptosis in acute myeloid leukemia through suppressing the IGF2BP3/MDM2 cascade.Ann Hematol. 2024 Nov;103(11):4511-4524. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-06003-4. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39264435
-
m6A-dependent upregulation of DDX21 by super-enhancer-driven IGF2BP2 and IGF2BP3 facilitates progression of acute myeloid leukaemia.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Apr;14(4):e1628. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1628. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38572589 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDF2 mediates the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressors to induce AKT phosphorylation in N6-methyladenosine-dependent way in prostate cancer.Mol Cancer. 2020 Oct 29;19(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01267-6. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33121495 Free PMC article.
-
The N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in acute myeloid leukemia.Curr Opin Hematol. 2021 Mar 1;28(2):80-85. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000636. Curr Opin Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33337619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The multifaceted nature of SUMOylation in heart disease and its therapeutic potential.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Aug;480(8):4725-4743. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05286-z. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40287894 Review.
-
RMVar 2.0: an updated database of functional variants in RNA modifications.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 6;53(D1):D275-D283. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae924. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39436017 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and Molecular Characterization of Potential RNA Binding Protein Involved in the Pathogenesis of Liver Ischemia Reperfusion Injury.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 22;17:4881-4893. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S468828. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39070133 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into SUMOylation and NEDDylation in fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 4;15:1476699. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1476699. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39697538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical force-induced oncostatin M secretion by Jun-positive neutrophils promotes craniofacial bone regeneration for midface hypoplasia treatment.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):330. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04458-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40598376 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

