Rapid identification of medicinal plants via visual feature-based deep learning
- PMID: 38822406
- PMCID: PMC11140858
- DOI: 10.1186/s13007-024-01202-6
Rapid identification of medicinal plants via visual feature-based deep learning
Abstract
Background: Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plants (CMPs) hold a significant and core status for the healthcare system and cultural heritage in China. It has been practiced and refined with a history of exceeding thousands of years for health-protective affection and clinical treatment in China. It plays an indispensable role in the traditional health landscape and modern medical care. It is important to accurately identify CMPs for avoiding the affected clinical safety and medication efficacy by the different processed conditions and cultivation environment confusion.
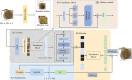
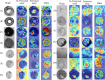
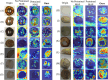
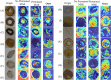
Results: In this study, we utilize a self-developed device to obtain high-resolution data. Furthermore, we constructed a visual multi-varieties CMPs image dataset. Firstly, a random local data enhancement preprocessing method is proposed to enrich the feature representation for imbalanced data by random cropping and random shadowing. Then, a novel hybrid supervised pre-training network is proposed to expand the integration of global features within Masked Autoencoders (MAE) by incorporating a parallel classification branch. It can effectively enhance the feature capture capabilities by integrating global features and local details. Besides, the newly designed losses are proposed to strengthen the training efficiency and improve the learning capacity, based on reconstruction loss and classification loss.
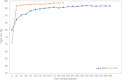
Conclusions: Extensive experiments are performed on our dataset as well as the public dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves the best performance among the state-of-the-art methods, highlighting the advantages of efficient implementation of plant technology and having good prospects for real-world applications.
Keywords: Deep learning; Identification; Image recognition; Masked autoencoders; Medicinal plants.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- China Pharmaceutical Technology Press . Pharmacopoeia of the people’s Republic of China, part 1, Ministry. Beijing: of Public Health of the People’s Republic of China; 2020.
Grants and funding
- 2021MS012/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS012/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS012/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 2021MS012/Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 61871277/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

