Exercise following joint distraction inhibits muscle wasting and delays the progression of post-traumatic osteoarthritis in rabbits by activating PGC-1α in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 38822418
- PMCID: PMC11141044
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-024-04803-y
Exercise following joint distraction inhibits muscle wasting and delays the progression of post-traumatic osteoarthritis in rabbits by activating PGC-1α in skeletal muscle
Abstract
Objective: Muscle wasting frequently occurs following joint trauma. Previous research has demonstrated that joint distraction in combination with treadmill exercise (TRE) can mitigate intra-articular inflammation and cartilage damage, consequently delaying the advancement of post-traumatic osteoarthritis (PTOA). However, the precise mechanism underlying this phenomenon remains unclear. Hence, the purpose of this study was to examine whether the mechanism by which TRE following joint distraction delays the progression of PTOA involves the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α), as well as its impact on muscle wasting.
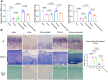
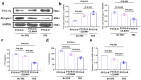
Methods: Quadriceps samples were collected from patients with osteoarthritis (OA) and normal patients with distal femoral fractures, and the expression of PGC-1α was measured. The hinged external fixator was implanted in the rabbit PTOA model. One week after surgery, a PGC-1α agonist or inhibitor was administered for 4 weeks prior to TRE. Western blot analysis was performed to detect the expression of PGC-1α and Muscle atrophy gene 1 (Atrogin-1). We employed the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique to examine pro-inflammatory factors. Additionally, we utilized quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) to analyze genes associated with cartilage regeneration. Synovial inflammation and cartilage damage were evaluated through hematoxylin-eosin staining. Furthermore, we employed Masson's trichrome staining and Alcian blue staining to analyze cartilage damage.
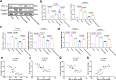
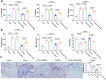
Results: The decreased expression of PGC-1α in skeletal muscle in patients with OA is correlated with the severity of OA. In the rabbit PTOA model, TRE following joint distraction inhibited the expressions of muscle wasting genes, including Atrogin-1 and muscle ring finger 1 (MuRF1), as well as inflammatory factors such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in skeletal muscle, potentially through the activation of PGC-1α. Concurrently, the production of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, nitric oxide (NO), and malondialdehyde (MDA) in the synovial fluid was down-regulated, while the expression of type II collagen (Col2a1), Aggrecan (AGN), SRY-box 9 (SOX9) in the cartilage, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the synovial fluid was up-regulated. Additionally, histological staining results demonstrated that TRE after joint distraction reduced cartilage degeneration, leading to a significant decrease in OARSI scores.TRE following joint distraction could activate PGC-1α, inhibit Atrogin-1 expression in skeletal muscle, and reduce C-telopeptides of type II collagen (CTX-II) in the blood compared to joint distraction alone.
Conclusion: Following joint distraction, TRE might promote the activation of PGC-1α in skeletal muscle during PTOA progression to exert anti-inflammatory effects in skeletal muscle and joint cavity, thereby inhibiting muscle wasting and promoting cartilage regeneration, making it a potential therapeutic intervention for treating PTOA.
Keywords: Exercise; Joint distraction; Muscle wasting; PGC-1α; Post-traumatic osteoarthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
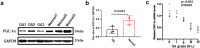
Similar articles
-
Intra-bone marrow injection of magnesium isoglyrrhizinate inhibits inflammation and delays osteoarthritis progression through the NF-κB pathway.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Aug 31;17(1):400. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03294-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 36045373 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on the protective mechanism of autophagy on cartilage by magnesium sulfate].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Oct 15;32(10):1340-1345. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201804015. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30600669 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Exercise-induced modulation of myokine irisin on muscle-bone unit in the rat model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Jan 9;19(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04532-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38195597 Free PMC article.
-
An Evidence-Based Systematic Review of Human Knee Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis (PTOA): Timeline of Clinical Presentation and Disease Markers, Comparison of Knee Joint PTOA Models and Early Disease Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 17;22(4):1996. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041996. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671471 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PGC-1α signaling in skeletal muscle health and disease.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Oct;1271(1):110-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06738.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 23050972 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

