Electroconvulsive therapy in N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis: A retrospective cohort and scoping review of literature
- PMID: 38823118
- PMCID: PMC11539951
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2024.578369
Electroconvulsive therapy in N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis: A retrospective cohort and scoping review of literature
Abstract
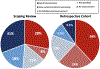
Neuropsychiatric symptoms in N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis (NMDARE) have led some to pursue empiric trials of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). A scoping review identified 39 patients diagnosed with NMDARE undergoing ECT. Separately, a retrospective cohort was reviewed to characterize 21 patients. Clinical improvement was attributed to ECT in 49% of patients in the scoping review and 19% of patients in the retrospective cohort; timing of immunotherapies was a confounding factor. Worsening of clinical course following ECT was reported in 28% of patients in the scoping review and 38% of patient in the retrospective review. There is currently insufficient data supporting a beneficial effect of ECT in NMDARE.
Keywords: Autoimmune encephalitis; Catatonia; Electroconvulsive therapy; N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis; Neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Diwani A, Handel A, Townsend L, Pollak T, Leite MI, Harrison PJ, Lennox BR, Okai D, Manohar SG, Irani SR, 2019. The psychopathology of NMDAR-antibody encephalitis in adults: a systematic review and phenotypic analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Psychiatry 6, 235–246. 10.1016/s2215-0366(19)30001-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources