Isolation of human antibodies against influenza B neuraminidase and mechanisms of protection at the airway interface
- PMID: 38823390
- PMCID: PMC11440431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.05.002
Isolation of human antibodies against influenza B neuraminidase and mechanisms of protection at the airway interface
Abstract
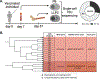
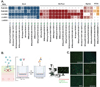
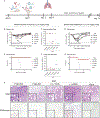
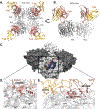
Influenza B viruses (IBVs) comprise a substantial portion of the circulating seasonal human influenza viruses. Here, we describe the isolation of human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that recognized the IBV neuraminidase (NA) glycoprotein from an individual following seasonal vaccination. Competition-binding experiments suggested the antibodies recognized two major antigenic sites. One group, which included mAb FluB-393, broadly inhibited IBV NA sialidase activity, protected prophylactically in vivo, and bound to the lateral corner of NA. The second group contained an active site mAb, FluB-400, that broadly inhibited IBV NA sialidase activity and virus replication in vitro in primary human respiratory epithelial cell cultures and protected against IBV in vivo when administered systemically or intranasally. Overall, the findings described here shape our mechanistic understanding of the human immune response to the IBV NA glycoprotein through the demonstration of two mAb delivery routes for protection against IBV and the identification of potential IBV therapeutic candidates.
Keywords: adaptive immunity; antibodies; human; influenza B; monoclonal; neuraminidase.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests L.E.W. serves as a consultant for BigHat Biosciences. The content of this article is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not represent the official views of BigHat Biosciences. C.B.C. serves as a consultant to GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, TDCowen Investments, Guidepoint Global, Debiopharm, and CommenseBio and receives royalties from UpToDate. The laboratory of C.B.C. receives funding for unrelated work from Moderna. J.E.C. has served as a consultant for Luna Labs USA, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corporation, Emergent Biosolutions, GlaxoSmithKline, and BTG International Inc; is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Meissa Vaccines; a former member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Gigagen (Grifols); and is founder of IDBiologics. The laboratory of J.E.C. received unrelated sponsored research agreements from AstraZeneca, Takeda, and IDBiologics during the conduct of the study. The opinions, interpretations, conclusions, and recommendations contained herein are those of the authors and are not necessarily endorsed by the US Department of Defense. E.D., T.E.E., and B.J.D. are employees of Integral Molecular, B.J.D. is a shareholder of Integral Molecular. Vanderbilt University has applied for a patent pertinent to some of the materials in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Broad and Protective Influenza B Virus Neuraminidase Antibodies in Humans after Vaccination and their Clonal Persistence as Plasma Cells.mBio. 2019 Mar 12;10(2):e00066-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00066-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30862743 Free PMC article.
-
Human Antibodies Targeting Influenza B Virus Neuraminidase Active Site Are Broadly Protective.Immunity. 2020 Oct 13;53(4):852-863.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.08.015. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32976769 Free PMC article.
-
Dual roles of influenza B virus neuraminidase mRNA vaccine in enhancing cross-lineage protection by supplementing inactivated split vaccination.J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0229424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02294-24. Epub 2025 Apr 23. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40265888 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza B virus neuraminidase: a potential target for next-generation vaccines?Expert Rev Vaccines. 2024 Jan-Dec;23(1):39-48. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2023.2290691. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 38037386 Review.
-
Anti-neuraminidase immunity in the combat against influenza.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2024 Jan-Dec;23(1):474-484. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2024.2343689. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 38632930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of an intranasal neuraminidase-based influenza vaccine with bacterial cell membrane-derived adjuvants.NPJ Vaccines. 2025 Jul 10;10(1):149. doi: 10.1038/s41541-025-01209-7. NPJ Vaccines. 2025. PMID: 40640198 Free PMC article.
-
Neuraminidase-specific antibodies drive differential cross-protection between contemporary FLUBV lineages.Sci Adv. 2025 Mar 28;11(13):eadu3344. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu3344. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40153499 Free PMC article.
-
Broad neuraminidase antibodies confer protection against seasonal and avian influenza viruses.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 2;16(1):7103. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62040-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40753167 Free PMC article.
-
Fast-Flu: RT-RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a assisted one-step platform for rapid influenza B virus detection.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jun 3;13(6):e0036525. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00365-25. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40277382 Free PMC article.
-
Single-domain antibodies directed against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase protect against influenza B viruses.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5831. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60232-3. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40593518 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

