Pembrolizumab for advanced urothelial carcinoma: exploratory ctDNA biomarker analyses of the KEYNOTE-361 phase 3 trial
- PMID: 38823511
- PMCID: PMC11405267
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03091-7
Pembrolizumab for advanced urothelial carcinoma: exploratory ctDNA biomarker analyses of the KEYNOTE-361 phase 3 trial
Abstract
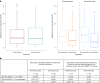
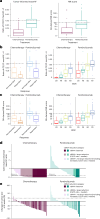
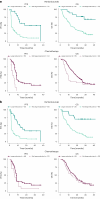
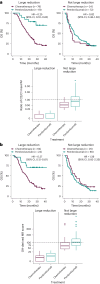
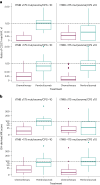
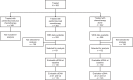
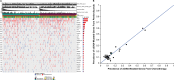
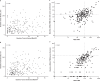
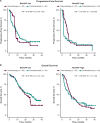
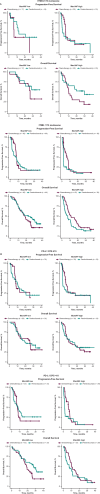
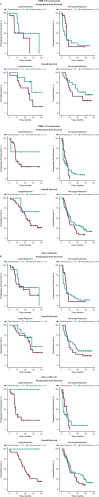
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is emerging as a potential biomarker in early-stage urothelial cancer, but its utility in metastatic disease remains unknown. In the phase 3 KEYNOTE-361 study, pembrolizumab with and without chemotherapy was compared with chemotherapy alone in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer. The study did not meet prespecified efficacy thresholds for statistical significance. To identify potential biomarkers of response, we retrospectively evaluated the association of pre- and posttreatment ctDNA with clinical outcomes in a subset of patients who received pembrolizumab (n = 130) or chemotherapy (n = 130) in KEYNOTE-361. Baseline ctDNA was associated with best overall response (BOR; P = 0.009), progression-free survival (P < 0.001) and overall survival (OS; P < 0.001) for pembrolizumab but not for chemotherapy (all; P > 0.05). Chemotherapy induced larger ctDNA decreases from baseline to treatment cycle 2 than pembrolizumab; however, change with pembrolizumab (n = 87) was more associated with BOR (P = 4.39 × 10-5) and OS (P = 7.07 × 10-5) than chemotherapy (n = 102; BOR: P = 1.01 × 10-4; OS: P = 0.018). Tumor tissue-informed versions of ctDNA change metrics were most associated with clinical outcomes but did not show a statistically significant independent value for explaining OS beyond radiographic change by RECIST v.1.1 when jointly modeled (pembrolizumab P = 0.364; chemotherapy P = 0.823). These results suggest distinct patterns in early ctDNA changes with immunotherapy and chemotherapy and differences in their association with long-term outcomes, which provide preliminary insights into the utility of liquid biopsies for treatment monitoring in metastatic urothelial cancer. Clinical trial registration: NCT02853305 .
© 2024. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates, and The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
T.P. reports receiving grants from AstraZeneca, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Ipsen, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Merck Serono, Astellas, Johnson & Johnson, and Eisai; consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Incyte, Ipsen, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Merck Serono, Astellas, Johnson & Johnson, Eisai, Roche, Mashup and Gilead; honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Incyte, Ipsen, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Merck Serono, Astellas, Johnson & Johnson, Eisai, Roche, Mashup and Gilead; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Roche, Pfizer, MSD, AstraZeneca, Ipsen, Gilead and Astellas; holds a strategic advisory role for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Ipsen, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Merck Serono, Astellas, Johnson & Johnson, Eisai and Roche; and holds a principal investigator role for Novartis, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Roche/Genentech, Eisai and Merck. J. Munoz reports receiving honoraria for presentations from LEO pharma and GlaxoSmithKline and support for attending meetings and/or travel from LEP Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca. A.P. reports receiving consulting fees from Astellas Pharma, Janssen-Cilag, Bayer, Novartis, Merck Serono, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, MSD Oncology, Takeda, AstraZeneca and Pfizer; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Pfizer, Astellas Pharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb and MSD; and honoraria from Astellas Pharma, Janssen Oncology, Bayer, Merck Serono, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Exelixis, MSD, Medison, Roche and AstraZeneca. E.Y.Y. reports consulting for Jansen, Merck, AAA Novartis, Bayer, Aadi Bioscience, Oncternal, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Loxo, and Lantheus, and receiving research grants to his institution from Dendreon, Merck, SeaGen, Blue Earth, Bayer – DAROL and citDNA, Lantheus, Tyra, Oncternal, Daiichi-Sankyo, Taiho and Surface. A.L. reports receiving consulting fees from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Esai, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche; honoraria from Astellas, Novartis and Healthbook Company Switzerland; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Ipsen, Janssen and Bayer; and holds a leadership or fiduciary role for European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines bladder cancer, European Society Medical Oncology (ESMO) faculty nonprostate, German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology (DGHO) guideline bladder and testis cancer, the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research (SAKK) scientific board committee and the National Center for Tumors (NCT) scientific board committee. A.B. is an employee of MSD, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., and holds stock in Merck & Co., Inc. B.H.M. is an employee of MSD, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., and holds stock in Merck & Co., Inc. J. Markensohn is an employee of MSD, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., and holds stock in Merck & Co., Inc. M.E. is an employee of MSD, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc. C.C. is an employee of MSD, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., and holds stock in Merck & Co., Inc. R.C. is an employee of MSD, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., and holds stock in Merck & Co., Inc. C.P. is an employee of MSD, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., and holds stock in Merck & Co., Inc. J.L. Is an employee of MSD, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., and holds stock in Merck & Co., Inc. Y.-H.C., Y.Y., F.R-C., G.P. and S.G. have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Utility of Serial Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis as a Minimally Invasive Biomarker in Advanced Urothelial Cancer.JCO Precis Oncol. 2025 Jan;9:e2400472. doi: 10.1200/PO-24-00472. Epub 2025 Jan 6. JCO Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39761498
-
Association of Tumor Mutational Burden and PD-L1 with the Efficacy of Pembrolizumab with or without Chemotherapy versus Chemotherapy in Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 2;30(23):5353-5364. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3518. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39475359 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of Histology on Clinical Outcomes of Pembrolizumab Monotherapy in Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma in the Phase 3 KEYNOTE-045 and KEYNOTE-361 Trials.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2025 Apr;23(2):102273. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2024.102273. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40037029 Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic significance of circulating tumor DNA in urothelial carcinoma patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 29;16:1574449. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1574449. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40364842 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of circulating tumor DNA in urothelial carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2024 Jun 1;110(6):3923-3936. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001372. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38573063 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multimodal integration of blood RNA and ctDNA reflects response to immunotherapy in metastatic urothelial cancer.JCI Insight. 2025 Jan 30;10(5):e186062. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.186062. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 39883530 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Monitoring of Circulating Tumor DNA to Predict the Risk of Non In Situ Recurrence of Postoperative Glioma: A Prospective Cohort Study.Cancer Med. 2025 Mar;14(5):e70733. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70733. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40022576 Free PMC article.
-
Early ctDNA and Survival in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Secondary Analysis of the SAMCO-PRODIGE 54 Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Oncol. 2025 Aug 1;11(8):874-882. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2025.1646. JAMA Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40531517 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Circulating Tumor DNA and Response to Cisplatin-based Chemotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma Enrolled in CALGB 90601 (Alliance).Eur Urol Open Sci. 2025 Apr 7;75:80-88. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2025.03.009. eCollection 2025 May. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2025. PMID: 40256659 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab adjuvant to chemo-radiation in localized muscle-invasive urothelial cancer: primary analysis of a multicenter, single-arm, phase II, investigator-initiated trial (NEXT).J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Mar 18;13(3):e010572. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010572. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40102029 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

