Underlying systemic mastocytosis in patients with unexplained osteoporosis: score proposal
- PMID: 38823568
- PMCID: PMC11854854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2024.117141
Underlying systemic mastocytosis in patients with unexplained osteoporosis: score proposal
Abstract
Background: A score to predict the association between unexplained osteoporosis and an underlying systemic Mastocytosis (SM) is lacking.
Objective: This study aimed at identifying criteria able to predict the diagnosis of SM without skin involvement and provide an indication for bone marrow (BM) assessment.
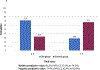
Methods: We included 139 adult patients with unexplained osteoporosis and suspected SM. After BM evaluation, 63 patients (45.3 %) were diagnosed with SM, while the remaining 76 patients (54.7 %) negative for clonal mast cell (MC) disorders, constituted our control group. Univariate and multivariate analysis identified three independent predictive factors: age (<54 years: +1 point, >64 years: -1 point), serum basal tryptase (sBT) levels >19 ng/mL (+2 points) and vertebral fractures (+2 points).
Results: These variables were used to build the OSTEO-score, able to predict the diagnosis of SM before BM assessment with a sensitivity of 73.5 % and a specificity of 67.1 %. Patients with a score < 3 had a lower probability of having SM compared to patients with a score ≥ 3 (28.5 % and 71.4 %, respectively, p < 0.0001). When sBT levels were corrected for the presence of hereditary alpha-tryptasemia (HαT) using the BST calculater (https://bst-calculater.niaid.nih.gov/) recently published [1,2], the sensitivity of ΗαT-adjusted OSTEO-score increased to 87.8 %, and the specificity reached 76.1 %. Also, the positive predictive value of a score ≥ 3 increased to 85.2 %.
Conclusions: Further studies are needed to validate these results and characterize the role of tryptase genotyping in patients with unexplained osteoporosis in reducing the risk of misdiagnosing patients with SM. Our proposed scoring model allows the identification of patients with the highest probability of having SM, avoiding unnecessary BM studies.
Keywords: Bone marrow mastocytosis; Hereditary alpha tryptasemia; Predictive score; Severe osteoporosis; Systemic mastocytosis.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All the authors have approved this manuscript and declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Chovanec J, Tunc I, Hughes J, Halstead J, Mateja A, Liu Y, O’Connell MP, Kim J, Park YH, Wang Q, Le Q, Pirooznia M, Trivedi NN, Bai Y, Yin Y, Hsu AP, McElwee J, Lassiter S, Nelson C, Bandoh J, DiMaggio T, Šelb J, Rijavec M, Carter MC, Komarow HD, Sabato V, Steinberg J, Hafer KM, Feuille E, Hourigan CS, Lack J, Khoury P, Maric I, Zanotti R, Bonadonna P, Schwartz LB, Milner JD, Glover SC, Ebo DG, Korošec P, Caughey GH, Brittain EH, Busby B, Metcalfe DD, Lyons JJ, Genetically defined individual reference ranges for tryptase limit unnecessary procedures and unmask myeloid neoplasms, Blood Adv 7 (2023) 1796–1810. 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007936. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Valent P, Akin C, Escribano L, Födinger M, Hartmann K, Brockow K, Castells M, Sperr WR, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Hamdy N. a. T., Lortholary O, Robyn J, Doormaal JV, Sotlar K, Hauswirth AW, Arock M, Hermine O, Hellmann A, Triggiani M, Niedoszytko M, Schwartz LB, Orfao A, Horny H-P, Metcalfe DD, Standards and standardization in mastocytosis: Consensus Statements on Diagnostics, Treatment Recommendations and Response Criteria, European Journal of Clinical Investigation 37 (2007) 435–453. 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2007.01807.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

