IκBα controls dormancy in hematopoietic stem cells via retinoic acid during embryonic development
- PMID: 38824124
- PMCID: PMC11144194
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48854-5
IκBα controls dormancy in hematopoietic stem cells via retinoic acid during embryonic development
Abstract
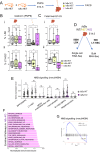
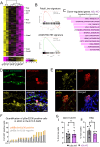
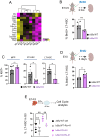
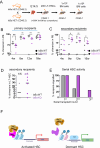
Recent findings suggest that Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSC) and progenitors arise simultaneously and independently of each other already in the embryonic aorta-gonad mesonephros region, but it is still unknown how their different features are established. Here, we uncover IκBα (Nfkbia, the inhibitor of NF-κB) as a critical regulator of HSC proliferation throughout development. IκBα balances retinoic acid signaling levels together with the epigenetic silencer, PRC2, specifically in HSCs. Loss of IκBα decreases proliferation of HSC and induces a dormancy related gene expression signature instead. Also, IκBα deficient HSCs respond with superior activation to in vitro culture and in serial transplantation. At the molecular level, chromatin regions harboring binding motifs for retinoic acid signaling are hypo-methylated for the PRC2 dependent H3K27me3 mark in IκBα deficient HSCs. Overall, we show that the proliferation index in the developing HSCs is regulated by a IκBα-PRC2 axis, which controls retinoic acid signaling.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Polycomb repressive complex 2 regulates normal hematopoietic stem cell function in a developmental-stage-specific manner.Cell Stem Cell. 2014 Jan 2;14(1):68-80. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Cell Stem Cell. 2014. PMID: 24239285 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid signaling is essential for embryonic hematopoietic stem cell development.Cell. 2013 Sep 26;155(1):215-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.055. Cell. 2013. PMID: 24074870
-
Mpl receptor defect leads to earlier appearance of hematopoietic cells/hematopoietic stem cells in the Aorta-Gonad-Mesonephros region, with increased apoptosis.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(6-7):1067-74. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.103104mf. Int J Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20711984
-
Role of the microenvironment of the embryonic aorta-gonad-mesonephros region in hematopoiesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Jun;938:109-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03579.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11458497 Review.
-
Embryonic beginnings of adult hematopoietic stem cells.Haematologica. 2005 Jan;90(1):100-8. Haematologica. 2005. PMID: 15642676 Review.
Cited by
-
p65 signaling dynamics drive the developmental progression of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells through cell cycle regulation.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 6;15(1):7787. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51922-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39242546 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of placental hemogenic endothelial cells to hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.Cell Discov. 2025 Jan 28;11(1):9. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00760-2. Cell Discov. 2025. PMID: 39875377 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PID2022-137945OB-I00/Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness | Agencia Estatal de Investigación (Spanish Agencia Estatal de Investigación)
- PID2019-104695RB-I00/Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness | Agencia Estatal de Investigación (Spanish Agencia Estatal de Investigación)
- 2021SGR00039/Departament d'Innovació, Universitats i Empresa, Generalitat de Catalunya (Department of Innovation, Education and Enterprise, Government of Catalonia)
- BP2016(00021)/Departament d'Innovació, Universitats i Empresa, Generalitat de Catalunya (Department of Innovation, Education and Enterprise, Government of Catalonia)
- BP2018(00034)/Departament d'Innovació, Universitats i Empresa, Generalitat de Catalunya (Department of Innovation, Education and Enterprise, Government of Catalonia)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

