Predictive value of triglyceride glucose index combined with neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for major adverse cardiac events after PCI for acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
- PMID: 38824158
- PMCID: PMC11144263
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63604-9
Predictive value of triglyceride glucose index combined with neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for major adverse cardiac events after PCI for acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Abstract
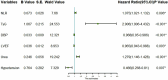
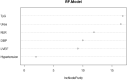
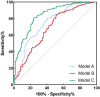
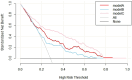
Acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a severe cardiovascular disease that poses a significant threat to the life and health of patients. This study aimed to investigate the predictive value of triglyceride glucose index (TyG) combined with neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) for in-hospital cardiac adverse event (MACE) after PCI in STEMI patients. From October 2019 to June 2023, 398 STEMI patients underwent emergency PCI in the Second People's Hospital of Hefei. Stepwise regression backward method and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to screen the independent risk factors of MACE in STEMI patients. To construct the prediction model of in-hospital MACE after PCI in STEMI patients: Grace score model is the old model (model A); TyG combined with NLR model (model B); Grace score combined with TyG and NLR model is the new model (model C). We assessed the clinical usefulness of the predictive model by comparing Integrated Discrimination Improvement (IDI), Net Reclassification Index (NRI), Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC), and Decision Curve Analysis (DCA). Stepwise regression and multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that TyG and NLR were independent risk factors for in-hospital MACE after PCI in STEMI patients. The constructed Model C was compared to Model A. Results showed NRI 0.5973; NRI + 0.3036, NRI - 0.2937, IDI 0.3583. These results show that the newly developed model C predicts the results better than model A, indicating that the model is more accurate. The ROC analysis results showed that the AUC of Model A for predicting MACE in STEMI was 0.749. Model B predicted MACE in STEMI with an AUC of 0.685. Model C predicted MACE in STEMI with an AUC of 0.839. For DCA, Model C has a better net return between threshold probability 0.1 and 0.78, which is better than Model A and Model B. In this study, by combining TyG, NLR, and Grace score, it was shown that TyG combined with NLR could reasonably predict the occurrence of MACE after PCI in STEMI patients and the clinical utility of the prediction model.
Keywords: Acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; MACE; NLR; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Percutaneous coronary intervention; STEMI; Triglyceride glucose index; TyG.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment and validation of a nomogram model containing a triglyceride-glucose index and neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio for predicting major adverse cardiac events in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.J Int Med Res. 2024 Sep;52(9):3000605241258181. doi: 10.1177/03000605241258181. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39291425 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of novel inflammatory markers combined with GRACE score for in-hospital outcome in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a retrospective observational study.BMJ Open. 2025 Apr 3;15(4):e096621. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-096621. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40180376 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and mean platelet volume in the prediction of adverse events after primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Atherosclerosis. 2018 Jul;274:212-217. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.05.022. Epub 2018 May 17. Atherosclerosis. 2018. PMID: 29803159
-
Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 May 2;18(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0812-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 29716535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 28;103(26):e38692. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038692. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38941418 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Value of Triglyceride Glucose Index in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Key Predictor of Mortality and Thrombus Burden.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;14(20):2261. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14202261. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451584 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Inhospital Cardiac Events in Geriatric Patients With Hip Fractures.Mediators Inflamm. 2024 Dec 17;2024:5587265. doi: 10.1155/mi/5587265. eCollection 2024. Mediators Inflamm. 2024. PMID: 39723114 Free PMC article.
-
The Predictive Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index for Cardiovascular Events in Chronic Total Occlusion Patients Who Prior Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Nov 9;17:8611-8623. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S486692. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39539724 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of cardiac deterioration in acute heart failure patients: Evaluation of the efficacy of single laboratory indicator models versus comprehensive models.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 1;103(44):e40266. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040266. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39496050 Free PMC article.
-
A Clinical Retrospective Study on the Combined Use of Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Triglyceride-Glucose Index to Predict the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease.Cardiol Res. 2025 Apr;16(2):110-119. doi: 10.14740/cr2006. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Cardiol Res. 2025. PMID: 40051668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, Antunes MJ, Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Bueno H, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur. Heart J. 2018;39(2):119–177. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx393. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khera S, Kolte D, Gupta T, Subramanian KS, Khanna N, Aronow WS, et al. Temporal trends and sex differences in revascularization and outcomes of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in younger adults in the United States. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015;66(18):1961–1972. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.08.865. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abbate A, Wohlford GF, Del Buono MG, Chiabrando JG, Markley R, Turlington J, et al. Interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra and heart failure following ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: Results from a pooled analysis of the VCUART clinical trials. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2022;8(5):503–510. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvab075. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

