Pharmacokinetic and neuroimmune pharmacogenetic impacts on slow-release morphine cancer pain control and adverse effects
- PMID: 38824169
- PMCID: PMC11144121
- DOI: 10.1038/s41397-024-00339-w
Pharmacokinetic and neuroimmune pharmacogenetic impacts on slow-release morphine cancer pain control and adverse effects
Abstract
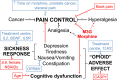
The aim was to determine if opioid neuroimmunopharmacology pathway gene polymorphisms alter serum morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide and morphine-6-glucuronide concentration-response relationships in 506 cancer patients receiving controlled-release oral morphine. Morphine-3-glucuronide concentrations (standardised to 11 h post-dose) were higher in patients without pain control (median (interquartile range) 1.2 (0.7-2.3) versus 1.0 (0.5-1.9) μM, P = 0.006), whereas morphine concentrations were higher in patients with cognitive dysfunction (40 (20-81) versus 29 (14-60) nM, P = 0.02). TLR2 rs3804100 variant carriers had reduced odds (adjusted odds ratio (95% confidence interval) 0.42 (0.22-0.82), P = 0.01) of opioid adverse events. IL2 rs2069762 G/G (0.20 (0.06-0.52)), BDNF rs6265 A/A (0.15 (0.02-0.63)) and IL6R rs8192284 carrier (0.55 (0.34-0.90)) genotypes had decreased, and IL6 rs10499563 C/C increased (3.3 (1.2-9.3)), odds of sickness response (P ≤ 0.02). The study has limitations in heterogeneity in doses, sampling times and diagnoses but still suggests that pharmacokinetics and immune genetics co-contribute to morphine pain control and adverse effects in cancer patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Randomized, Crossover Study on the Effect of Food on the Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Morphine ARER (MorphaBond™ ER), an Abuse-Deterrent Formulation of Extended-Release Morphine.Adv Ther. 2019 Sep;36(9):2394-2401. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01022-4. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 31278694 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Start of oral morphine to cancer patients: effective serum morphine concentrations and contribution from morphine-6-glucuronide to the analgesia produced by morphine.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2000 Jan;55(10):713-9. doi: 10.1007/s002280050003. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10663448
-
Population pharmacokinetics of oral morphine and its glucuronides in children receiving morphine as immediate-release liquid or sustained-release tablets for cancer pain.J Pediatr. 1999 Jul;135(1):47-55. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(99)70326-4. J Pediatr. 1999. PMID: 10393603
-
Opioids and the management of chronic severe pain in the elderly: consensus statement of an International Expert Panel with focus on the six clinically most often used World Health Organization Step III opioids (buprenorphine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone).Pain Pract. 2008 Jul-Aug;8(4):287-313. doi: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2008.00204.x. Epub 2008 May 23. Pain Pract. 2008. PMID: 18503626
-
A review of morphine and morphine-6-glucuronide's pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships in experimental and clinical pain.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015 Jul 10;74:45-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2015.03.020. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25861720 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

