ET1 acts as a potential plasma biomarker and therapeutic target in deep venous thrombosis rat model
- PMID: 38824487
- PMCID: PMC11315785
- DOI: 10.1007/s11239-024-02981-4
ET1 acts as a potential plasma biomarker and therapeutic target in deep venous thrombosis rat model
Abstract
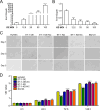
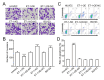
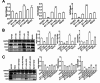
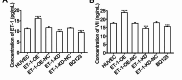
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is the third leading cause of death in cardiovascular disease, following heart attacks and strokes. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for effective DVT therapy. We aim to investigate whether endothelin-1 (ET-1) could serve as an early diagnostic marker or a potential therapeutic target in a DVT rat model. CCK8 assay, invasion assay, and flow cytometry were used to detect the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of HUVECs, respectively. Elisa assay was used to detect ET-1 and coagulation factor VII in cell supernatant and rat?s plasma. Western blot was used to detect antioxidant signaling protein. Inferior vena cava stenosis was used to construct the DVT rat model. Lentivirus mediated overexpression of ET-1 in HUVECs impaired the cell proliferation and migration, increased cell apoptosis, inhibited the antioxidant signaling pathway proteins expression (e.g., NQO1, GCLC, Nrf-2), and upregulated coagulation factor VII. Furthermore, overexpression of ET-1 further impaired antioxidant signaling pathway protein in response to H2O2 treatment. However, lentivirus mediated ET-1 knockdown and BQ123 (an ET-1 inhibitor), showed the opposite results with ET-1 overexpression. We then established a DVT rat model by inferior vena cava stenosis. The stenosis induced early expression of ET-1 and coagulation factor VII in plasma at day 1 and restore their level at day 10. BQ123 could downregulate the coagulation factor VII to ameliorate the stenosis effects. Our findings suggest that ET-1 might serve as an early diagnostic marker for DVT rat model and a potential therapeutic target for treating DVT.
Keywords: BQ123; Deep venous thrombosis; Diagnostic marker; Endothelin-1; The inferior vena cava stenosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerate angiogenesis in pregnant experimentally induced deep venous thrombosis rat model via up-regulation of pro-angiogenic secretogranin II.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 May;118:110025. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110025. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36933488
-
Mast Cells Granular Contents Are Crucial for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Mice.Circ Res. 2017 Sep 29;121(8):941-950. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311185. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28739590 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary clinical analysis and pathway study of S100A8 as a biomarker for the diagnosis of acute deep vein thrombosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 10;14(1):13298. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61728-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38858401 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulated miR-204-5p promoted the migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells to enhance the thrombolysis of rats with deep venous thrombosis by targeting SPRED1.Exp Cell Res. 2022 Feb 1;411(1):112985. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112985. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Exp Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 34942190
-
CREB1 Silencing Protects Against Inflammatory Response in Rats with Deep Vein Thrombosis Through Reducing RPL9 Expression and Blocking NF-κB Signaling.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024 Jun;17(3):570-584. doi: 10.1007/s12265-023-10450-1. Epub 2023 Oct 27. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 37891366
References
-
- Kucher N (2013) Deep-vein thrombosis of the Upper extremities. 364:861–869. 10.3238/arztebl.2017.0244 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

