Rebamipide gargle and benzydamine gargle in prevention and management of chemo-radiotherapy and radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients (randomized clinical trial)
- PMID: 38824583
- PMCID: PMC11143556
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-04379-3
Rebamipide gargle and benzydamine gargle in prevention and management of chemo-radiotherapy and radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients (randomized clinical trial)
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the preventive and therapeutic effects of rebamipide gargle in comparison with benzydamine in head and neck cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy.
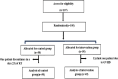
Materials and methods: Phase III randomized clinical trial was conducted from January 2021 till August 2022 on one hundred patients with head and neck cancer receiving high doses of radiotherapy. These patients were equally allocated into either rebamipide group or benzydamine group, The measured outcomes were the incidence of oral mucositis ≥ grade1, according to the WHO mucositis scale, in addition to the duration, and the onset of oral mucositis.
Results: There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups, regarding the incidence of a severe grade of oral mucositis (WHO grades 3), as well as the onset and duration of oral mucositis. Both gargles succeeded to prevent the development of WHO grade 4 oral mucositis. Side effects reported were mainly burning sensation in benzydamine group and nausea in rebamipide group.
Conclusion: Rebamipide mouthwash was as beneficial as benzydamine mouthwash in minimizing the incidence of severe oral mucositis induced by treatment of head and neck cancer. However, rebamipide gargle proved to be superior to benzydamine in terms of reduction in the severity of the radiation-induced oral mucositis.
Trial registration: The trial was registered in the protocol Registration and Result system of Clinical Trials (Registration ID: NCT04685395)0.28-12-2020.
Keywords: Benzydamine HCl; Chemoradiotherapy; Head & neck cancer; Oral mucositis; Radiotherapy; Rebamipide.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rebamipide gargle in preventive management of chemo-radiotherapy induced oral mucositis.Oral Oncol. 2017 Sep;72:179-182. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.07.024. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Oral Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28797456 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of benzydamine hydrochloride in the prevention of oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiotherapy (>50 Gy) with or without chemotherapy.Support Care Cancer. 2017 May;25(5):1439-1443. doi: 10.1007/s00520-016-3548-9. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Support Care Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27987094 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Aloe vera and Benzydamine Mouthwashes on Radiation-induced Oral Mucositis: A Triple-blind, Randomised, Controlled Clinical Trial.Oral Health Prev Dent. 2015;13(4):309-15. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.a33091. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2015. PMID: 25431805 Clinical Trial.
-
Potential prevention: Aloe vera mouthwash may reduce radiation-induced oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients.Chin J Integr Med. 2012 Aug;18(8):635-40. doi: 10.1007/s11655-012-1183-y. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Chin J Integr Med. 2012. PMID: 22855041 Review.
-
Management of radiation-induced oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients: a real-life survey among 25 Italian radiation oncology centers.Support Care Cancer. 2023 Dec 19;32(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-08185-5. Support Care Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38110572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gold nanoparticles as innovative therapeutics for oral mucositis: A review of current evidence.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jul;15(7):2323-2353. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01748-x. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39625578 Review.
-
Exploratory Research: Patient-Reported Factors Contributing to Decreased Oral Intake During Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer.Head Neck. 2025 Jun;47(6):1717-1725. doi: 10.1002/hed.28089. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Head Neck. 2025. PMID: 39854098 Free PMC article.
-
Benzydamine hydrochloride: an overview on a well-established drug with news in mechanisms of action.F1000Res. 2025 May 22;13:350. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.144067.2. eCollection 2024. F1000Res. 2025. PMID: 40585879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Treatments for Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Patients With Head and Neck Cancer.Cureus. 2025 Jun 16;17(6):e86145. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86145. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40671993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of herbal and benzydamine mouthwashes in preventing radiation-induced oral mucositis among head and neck cancer patients: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Evid Based Dent. 2025 Jun;26(2):118. doi: 10.1038/s41432-025-01117-8. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Evid Based Dent. 2025. PMID: 39948159
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

