Sex as a predictor of clinical phenotype and determinant of immune response in IgG4-related disease: a retrospective study of patients fulfilling the American College of Rheumatology-European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria
- PMID: 38824935
- PMCID: PMC11214762
- DOI: 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00089-4
Sex as a predictor of clinical phenotype and determinant of immune response in IgG4-related disease: a retrospective study of patients fulfilling the American College of Rheumatology-European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria
Abstract
Background: IgG4-related disease is a multiorgan fibroinflammatory disease considered to have an autoimmune origin. Case series describing individual organ involvement have suggested differences in phenotypic expression between males and females. We aimed to characterise differences in IgG4-related disease manifestations between male and female patients in a large single-centre cohort.
Methods: In this retrospective, single-centre cohort study, patients were recruited from the Massachusetts General Hospital Rheumatology Clinic (Boston, MA, USA) and classified according to the American College of Rheumatology-European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (ACR-EULAR) classification criteria. Only patients satisfying the ACR-EULAR classification criteria were included in the study. Data on age at diagnosis, organ involvement at baseline, treatment status, and pre-treatment laboratory values were collected. Circulating plasmablasts and B-cell subsets were quantitated by flow cytometry. Active disease was defined by an IgG4-related disease Responder Index score of more than 0. Laboratory values were analysed for patients who were untreated at baseline and had active IgG4-related disease. The main outcomes were assessed in all participants with available data.
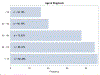
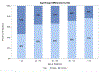
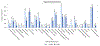
Findings: Of the 564 participants enrolled in the Massachusetts General Hospital Rheumatology Clinic IgG4-related disease Registry, 328 fulfilled ACR-EULAR classification criteria and were included between January, 2008, and May, 2023. There was a strong male predominance (male:female ratio 2·2:1) with 226 (69%) males and 102 (31%) females, which contrasted markedly with our general rheumatology clinic population (0·4:1; p<0·001). The male predominance increased with each decade of life starting at age 40 years. On average, male patients were 5·5 years older at diagnosis than female patients (63·7 years vs 58·2 years; p=0·0031). We observed male patients to have higher ACR-EULAR classification criteria scores at baseline with a median score of 35·0 (IQR 28·0-46·0), compared with 29·5 (25·0-39·0) for females (p=0·0010). The proportion of male patients with pancreatic and renal involvement was almost double the proportion observed in female patients (50% of the male patients had pancreatic involvement, compared with about 26% of the female patients; p<0·0001). Male patients were more likely to have serological abnormalities at baseline. The distribution of IgG4 values differed significantly between male an female sexes, favouring higher values in males. We found that male patients with IgG4-related disease were more likely to have active B-cell responses in the blood as defined by plasmablast expansions.
Interpretation: IgG4-related disease is unusual among autoimmune diseases in that it is more likely to affect males than females and to present with a striking sex-dependent organ distribution and degree of B-cell response. These findings highlight important variation between IgG4-related disease and other conditions generally believed to have an autoimmune basis. Most autoimmune diseases, by contrast to IgG4-related disease, demonstrate pronounced predilections for affecting females more frequently than males. Hypotheses surrounding the cause and pathophysiology of this condition need to consider this unusual sex distribution among patients with IgG4-related disease.
Funding: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Rheumatology Research Foundation, and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests YGHB reports honorarium from Otsuka-Visterra for continuing medical education and Grand Rounds lectures on autoimmune pancreatitis. ZSW reports consulting fees from Viela Bio, Zenas, Horizon, Sanofi, MedPace, BioCryst, and Amgen; and participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for Sanofi, Horizon, Novartis, Shionogi, and Otsuka-Visterra. SP reports consultancy fees from Be Bio Pharma, Paratus, and Octagon Therapeutics; and stock options for Ab Pro, Be Bio Pharma, and Paratus. JHS reports consultancy fees from Acepodia, Alexion, Bristol Myers Squibb, Connect Biopharma, Horizon, iCell Gene Therapeutics, Q32, Sanofi, and ZenasBio; has a role as Principal Investigator in a phase 3 clinical trial (inebilizumab); and is a consultant for Horizon (now Amgen) on IgG4-related disease. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
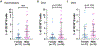
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Defining pancreatic damage and symptom burden in IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis: A cross-sectional study of 118 patients from a single-center registry.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2025 Aug;73:152742. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2025.152742. Epub 2025 May 21. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2025. PMID: 40403524
-
IgG4-related disease and other fibro-inflammatory conditions.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025 May;21(5):275-290. doi: 10.1038/s41584-025-01240-x. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40195520 Review.
-
Immunosuppressants for IgG4-related disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Aug 21;8(8):CD016094. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD016094. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40838448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med, 2012; 366:539–55. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Wallace ZS, Harvey L, et al. Prostate and pancreas involvement are linked in IgG4-related disease. Semin Arthr Rheum, 2020; 50:1245–51. - PubMed
-
- Wallace ZS, Nade RP, Chari S, et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2020; 72(1):7–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

