Cell-free DNA for the detection of kidney allograft rejection
- PMID: 38824959
- PMCID: PMC11333280
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03087-3
Cell-free DNA for the detection of kidney allograft rejection
Abstract
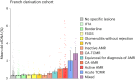
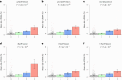
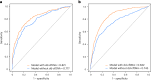
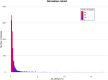
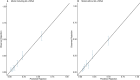
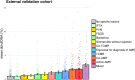
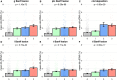
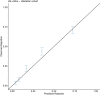
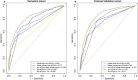
Donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA) is an emerging noninvasive biomarker that has the potential to detect allograft injury. The capacity of dd-cfDNA to detect kidney allograft rejection and its added clinical value beyond standard of care patient monitoring is unclear. We enrolled 2,882 kidney allograft recipients from 14 transplantation centers in Europe and the United States in an observational population-based study. The primary analysis included 1,134 patients. Donor-derived cell-free DNA levels strongly correlated with allograft rejection, including antibody-mediated rejection (P < 0.0001), T cell-mediated rejection (P < 0.0001) and mixed rejection (P < 0.0001). In multivariable analysis, circulating dd-cfDNA was significantly associated with allograft rejection (odds ratio 2.275; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.902-2.739; P < 0.0001) independently of standard of care patient monitoring parameters. The inclusion of dd-cfDNA to a standard of care prediction model showed improved discrimination (area under the curve 0.777 (95% CI 0.741-0.811) to 0.821 (95% CI 0.784-0.852); P = 0.0011) and calibration. These results were confirmed in the external validation cohorts (n = 1,748) including a cohort of African American patients (n = 439). Finally, dd-cfDNA showed high predictive value to detect subclinical rejection in stable patients. Our study provides insights on the potential value of assessing dd-cfDNA, in addition to standard of care monitoring, to improve the detection of allograft rejection. ClinicalTrials.gov registration: NCT05995379 .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

